Quick Intro: PhpCompatibility for PHPCS

Key Takeaways
- PHPCompatibility is a tool that can be installed on top of PHPCS to check a project’s compatibility with both newer and older versions of PHP. It supports PHP versions up to PHP 7.
- The tool can be installed via Pear or Composer, and once installed, can be used to check the compatibility of a project with a specific PHP version by running a specific command. The tool can also be fine-tuned to focus on errors, check only the local directory, show progress of the run, and ignore certain files or folders.
- PHPCompatibility is crucial for developers as it helps ensure their code is compatible with the PHP version they’re using or planning to use, preventing potential issues from using deprecated or unsupported PHP features and improving the overall quality and reliability of the code.
Sooner or later, there will come a time when you will need to migrate your projects to different PHP versions. How will you check if you’re compatible with a PHP version different to the one you’ve been developing on?
One possibility is always to install the version of PHP we want to migrate to, run php -l or something like PHPSA to check for syntax errors, check the PHP documentation for known issues with the migration and hope for the best. Or, we can use some available third party tools to check for PHP version compatibility in our projects.
![]()
Check compatibility with PHPCompatibility
PHPCompatibility is a set of sniffs we can install on top of PHPCS. This tool allows us to check our project’s compatibility with both newer and older versions of PHP. If you are not familiar with PHP QA tools, PHPCS is a tool which inspects PHP, JavaScript, and CSS for different code violations based on different sets of coding standards.
The current iteration of PHPCompatibility supports PHP versions up to PHP 7.
Installing PHPCompatibility
PHPCompatibility can be installed via Pear or via Composer. For this particular case, we will install PHPCS using Composer and then deploy our PHPCompatibility coding standards directly on top of it.
For a local installation:
composer require "squizlabs/php_codesniffer=2.*"
After PHPCS is installed, let’s move into the PHPCS /Standards folder that’s located in /vendor/squizlabs/php_codesniffer/CodeSniffer/Standards and run:
git clone https://github.com/wimg/PHPCompatibility.git
This command will deploy the PHPCompatibility coding standard directly into our standards folder, together with the coding standards already bundled in PHPCS. To check if both PHPCS and PHPCompatibility were successfully installed just run the command:
./vendor/bin/phpcs -i
This will list all the installed standards. We should see PHPCompatibility among them.
For a global installation, the same method is valid, just be sure to use Composer’s global require:
composer global require "squizlabs/php_codesniffer=2.*"
and then clone PHPCompatibility into the following folder:
~/.composer/vendor/squizlabs/php_codesniffer/CodeSniffer/Standards
Using PHPCS
If you never used PHPCS before, it is always good to start with ./vendor/bin/phpcs -h. This will show us the PHPCS help section.
Before we delve into the use of the PHPCompatibility standard, there are some PHPCS commands that will help us make our compatibility tests faster, more efficient and in line with the results we need:
-i– do not print warnings. This option will be helpful if we have a long list of messages and want to filter out the warnings to focus on the errors.-l– will only check the local directory, without recursion.-p– show progress of the run. Especially useful for big projects, to maintain status.-i– show the list of installed coding standards.<file>– the file or folder to check.<extensions>– a comma separated list of file extensions to check.<generator>– uses either theHTML,MarkdownorTextgenerator. It forces documentation generation instead of just doing the check.<patterns>– a comma separated list of patterns to ignore files and folders (e.g.vendor).<severity>– the minimum severity of a problem required to display an error or warning.<standard>– the name or path of the coding standard to use.<runtime-set>– some individual standards also require particular configuration options, which is also the case with PHPCompatibility. This command’s syntax is as follows:phpcs --runtime-set <option> <value>`
This list is far from exhaustive, but should be of great use in fine tuning our checks.
Checking compatibility
To check compatibility we can run the following command:
./vendor/bin/phpcs --standard=PHPCompatibility --runtime-set testVersion 7 <path>
With this command, we are using the PHPCompatibility standard with the runtime-set option we saw earlier. We are checking for compatibility with PHP 7 on the file or folder defined by <path>.
The tool will output something similar to this:
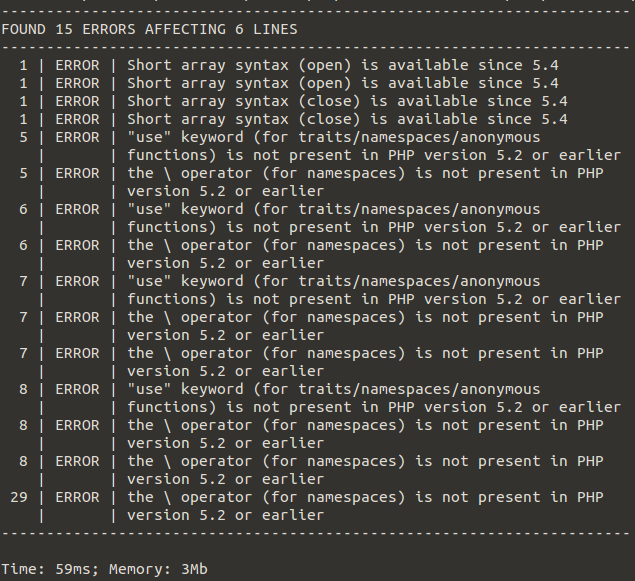
Note that if you are testing backwards compatibility, it is advisable that you execute PHPCS on the latest PHP version available. For example, if you have the keyword yield in your code, PHPCS can only recognize it if you’re running PHP 5.5 or higher on your machine. It will only tell you it is not available in previous PHP versions if it actually knows what it is.
If we want to test for .php files only, we can use the <extensions> option. Adding it to the command we used earlier:
./vendor/bin/phpcs --standard=PHPCompatibility --extensions=php --runtime-set testVersion 7 <path>
For a detailed report we can use the option --report-full=<path>.txt.
To ignore files or folders in the compatibility test (for example, the aforementioned vendor folder, and a folder with tests) we can use the option --ignore=*/tests/*,*/vendor/* <path>. This way, the designated files and folders will not be tested for compatibility.
All the PHPCS options we saw earlier can be used to help make a better use of the tool.
A real life example
Of course, we also want to know if this tool can help us with a real life, production type application. Let’s use it on a complex application to see the results. I’ve chosen PHPMailer for this one.
git clone https://github.com/PHPMailer/PHPMailer.git mailer
cd mailer
composer install
This will clone PHPMailer into the /mailer folder and install all its dependencies. After that, we need to install both PHPCS and the PHPCompatibility standard:
composer require "squizlabs/php_codesniffer"
cd vendor/squizlabs/php_codesniffer/CodeSniffer/Standards
git clone https://github.com/wimg/PHPCompatibility.git
Finally, lets run the PHPCompatibility standard on a single file (we can now also run it on the whole project, but let’s use a single file for this demonstration).
./vendor/bin/phpcs --standard=PHPCompatibility --extensions=php --runtime-set testVersion 5.6 class.phpmailer.php
As we can see, even though PHPMailer is not quite PHP 5.6 ready, we have all the information needed to upgrade the code.
Hope this quick tip tool introduction helped! How do you test for compatibility?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about PHPCompatibility Standard for PHPCS
What is PHPCompatibility and why is it important?
PHPCompatibility is a set of sniffs for PHP CodeSniffer that can check your code for compatibility with specific PHP versions. It’s crucial because it allows developers to ensure their code is compatible with the PHP version they’re using or planning to use. This helps to prevent potential issues that could arise from using deprecated or unsupported PHP features, thus improving the overall quality and reliability of the code.
How can I install PHPCompatibility?
PHPCompatibility can be installed using Composer, a dependency management tool for PHP. You can install it by running the command composer require --dev phpcompatibility/php-compatibility. After installation, you can add the PHPCompatibility standard to PHP CodeSniffer by using the command phpcs --config-set installed_paths /path/to/PHPCompatibility.
How do I use PHPCompatibility to check my code?
After installing PHPCompatibility, you can use it to check your code by running the command phpcs -p . --standard=PHPCompatibility. This command will check all PHP files in the current directory and its subdirectories. You can specify the PHP version you want to check against by adding --runtime-set testVersion X.Y to the command, where X.Y is the PHP version.
What does PHPCompatibility check for?
PHPCompatibility checks for a wide range of potential compatibility issues, including deprecated functions, removed functions, new functions, changed functions, deprecated INI directives, removed INI directives, new INI directives, deprecated constants, removed constants, new constants, deprecated language constructs, removed language constructs, new language constructs, and more.
Can PHPCompatibility check for compatibility with multiple PHP versions?
Yes, PHPCompatibility can check for compatibility with multiple PHP versions. You can specify the PHP versions you want to check against by adding --runtime-set testVersion X.Y-Z.A to the command, where X.Y is the minimum PHP version and Z.A is the maximum PHP version.
Can I exclude certain sniffs when using PHPCompatibility?
Yes, you can exclude certain sniffs when using PHPCompatibility. You can do this by adding --exclude=sniff1,sniff2,sniff3 to the command, where sniff1, sniff2, sniff3 are the sniffs you want to exclude.
How can I fix the issues reported by PHPCompatibility?
PHPCompatibility only reports potential compatibility issues, it doesn’t fix them. To fix the issues, you need to manually update your code to use the correct PHP features. You can use the PHP manual and other online resources to learn about the correct usage of PHP features.
Can PHPCompatibility be used with other PHP CodeSniffer standards?
Yes, PHPCompatibility can be used with other PHP CodeSniffer standards. You can specify multiple standards by adding --standard=standard1,standard2,standard3 to the command, where standard1, standard2, standard3 are the standards you want to use.
Can PHPCompatibility be used in continuous integration (CI) environments?
Yes, PHPCompatibility can be used in CI environments. You can add the PHPCompatibility check command to your CI configuration file to automatically check your code for compatibility issues whenever you push changes to your repository.
Is PHPCompatibility actively maintained and updated?
Yes, PHPCompatibility is actively maintained and updated. The maintainers regularly add new sniffs for new PHP features and changes, ensuring that PHPCompatibility stays up-to-date with the latest PHP versions.
Cláudio Ribeiro is a software developer, traveler, and writer from Lisbon. He's the author of the book An IDE Called Vim. When he is not developing some cool feature at Kununu he is probably backpacking somewhere in the world or messing with some obscure framework.

Published in
·automation·Debugging & Deployment·Development Environment·Libraries·Performance·PHP·Standards·Testing·September 7, 2016

Published in
·APIs·automation·CMS & Frameworks·Frameworks·Laravel·Libraries·Patterns & Practices·PHP·Standards·February 25, 2017



