14 Free Tools To Validate Your HTML, CSS & RSS Feeds
Key Takeaways
- The article lists 14 free tools for validating HTML, CSS, and RSS feeds, including both online tools and Firefox extensions, to help fix errors and ensure content is displayed as intended.
- The importance of validating HTML, CSS, and RSS feeds is highlighted, emphasizing accessibility for all users, identification and rectification of coding errors, and adherence to the latest web standards for improved search engine ranking.
- The article also provides answers to frequently asked questions about HTML, CSS, and RSS Feed Validation, explaining how validators work, the differences between HTML and CSS validation, and how to fix validation errors.
There can be nothing more disturbing than creating and styling a web page, thinking that you have it perfect, and then when testing it hitting upon some unknown display error that you simply can’t figure out. One of the tricks to fixing errors like this is to validate your markup and style sheets first. Luckily, there are numerous free tools out there to check whether your HTML, CSS and even your RSS feeds are valid. With these handy helpers, you can ensure that your visitors are experiencing your content exactly as you intend them to.
We’ve gathered up a mixture of 14 tools — both online tools and some Firefox extensions — so you can find the one that best suits your needs.
Firefox Plugins
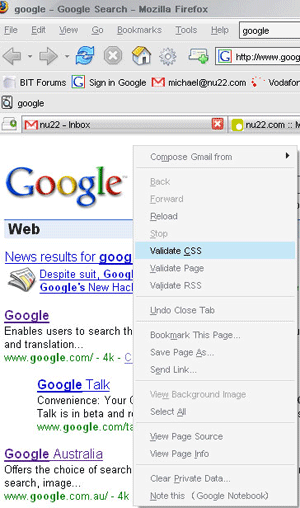
CSS Validator: Adds an easy-to-use link to the W3C CSS validator that you can access via a right-click context menu or from under the Tools menu.
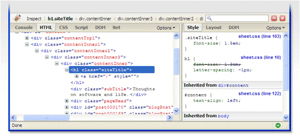
Firebug: Firebug is a full-featured debugger and editor that allows you to work with a page’s HTML, JavaScript, CSS, DOM and more. You can also use the extension to monitor JavaScript, CSS, and XML in real time, look for errors that may be occurring in them, and learn what you need to do to repair them. An essential tool in just about every designer’s arsenal of tools, Firebug has become so commonplace that it has even begun getting its own extensions (such as SitePoint’s own CodeBurner reference tool).
HTML Validator: Based on Tidy and OpenSP, HTML Validator gives you an easy icon notification of the validity of any page you are visiting. You can request more information from the tool, and when you view Page Source, errors causing the page to be invalid are highlighted. Even better, if you can’t figure out what’s wrong on your own, the extension will make suggestions for you.
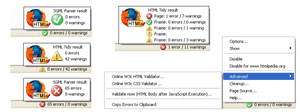
Page Validator: Either by opening the right-click context menu, or going up to tools and selecting “Validate Page”, Page Validator opens a separate tab and shows you the results using the the W3C’s online validation tool.
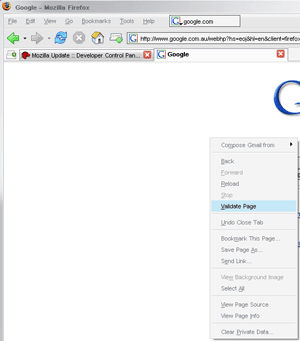
RSS Validator: RSS Validator allows you to easily check the validity of an RSS feed by using the right-click context menu or by making the choice from the tools menu. You are then sent to a separate tab to see the results and any potential errors.
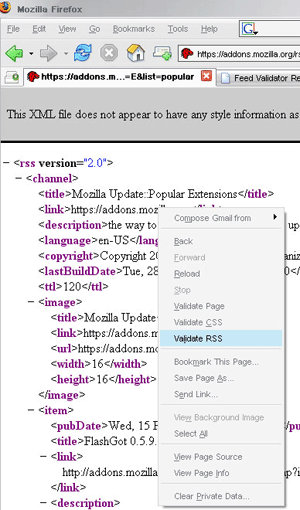
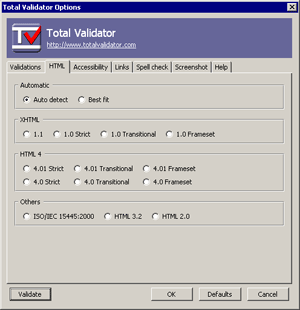
Total Validator: Total Validator gives you a ton of tools in one handy extension. Browse to the page you want, click the “TV” icon and validate it against multiple versions of HTML, spellcheck it, take screenshots and more.
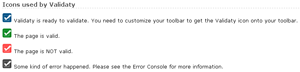
Validaty: Validaty allows you to add a button to your toolbar that will allow you to simply click it while visiting a page and view a simple visual representation to the validity of the page.
Web Based Validators
validator.w3.org: The W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) is the group that develops all of the standards for Web technologies, so it only makes sense that they would have a validator to check whether your HTML is correct. The file to be checked can be online or uploaded, and the validator can display its report in multiple formats — with recommendations, as an outline, with recommendations, and more. If you’re going to check your markup, it may as well be with the people who decree what works.
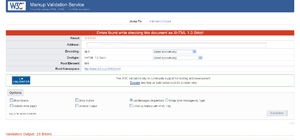
jigsaw.w3.org: The W3C also offer a CSS validation tool, which will also check your markup for any potential errors and warnings. You also have the option of setting different CSS profiles, specifying the medium that the style sheet was created for, and controlling how much information the report should display.
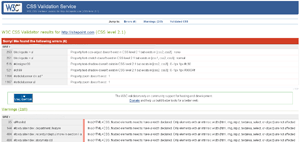
FeedValidator.org: FeedValidator will first make sure that the feed you pass it is valid, and then go through your most recent entries and give you a summary of problems, highlighting the actual lines where the problems exist. Very handy for making sure your feed displays correctly in various readers.
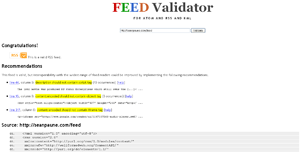
Relaxed.vse.cz: Relaxed does not use the official W3C specifications for validation, but instead uses some of its own to check out your document. You can choose which version of HTML for it to use, whether to display the source code, use a “dirty” parser, and there are a couple of other options. It is also available as a Firefox plugin, which adds the service directly to your browser.
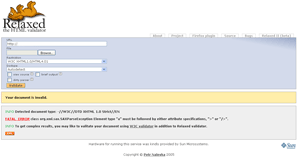
Validome.org: Validome is like your one-stop shop for validators. This site offers tools for checking out your HTML, XML, DTD-Schema, RSS and Google Sitemaps. Each tool provides numerous options so that you can set it to best suit your needs.
VirtualPromote.com: VirtualPromote provides developers with numerous tools for different jobs, but the three important ones for front-end developers are the HTML, CSS and XML validators.
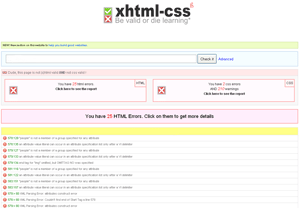
xhtml-css.com: xhtml-css.com gives any site a quick once-over, validating both the HTML and CSS in one go. The service will list any errors and possible warnings you may need to be aware of, and provide details about the nature of the problem. You can also use more advanced options to set different character encoding settings for your HTML, and for the CSS you can set the profile and medium that the stylesheet will be used for. The site also provides a Firefox extension called BeValid, that will let you validate the URL are currently visiting to speed up the process even more.
What’s your favorite validation tool?
Frequently Asked Questions about HTML, CSS, and RSS Feed Validation
What is the importance of validating HTML, CSS, and RSS feeds?
Validating your HTML, CSS, and RSS feeds is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that your website or web application is accessible to all users, including those using assistive technologies. Secondly, it helps to identify and fix any coding errors that could potentially affect your site’s performance or functionality. Lastly, it ensures that your site adheres to the latest web standards, which can improve its search engine ranking.
How does the W3C validator work?
The W3C validator is a free online tool that checks the markup validity of web documents in HTML, XHTML, SMIL, MathML, etc. It works by comparing your code against the formal grammar rules or “schemas” defined by the W3C, the organization responsible for developing web standards. If your code doesn’t adhere to these rules, the validator will highlight the errors and provide suggestions for fixing them.
What is the difference between HTML and CSS validation?
HTML validation checks the syntax and structure of your HTML code to ensure it adheres to the standards set by the W3C. On the other hand, CSS validation checks your CSS code for any errors or inconsistencies and ensures it complies with the CSS standards. Both are important for ensuring your website or web application works correctly and looks consistent across different browsers and devices.
How can I validate my RSS feeds?
You can validate your RSS feeds using an RSS validator tool. These tools work by checking your RSS feed for any errors or inconsistencies that could prevent it from being properly read by RSS readers. They can also provide suggestions for improving the structure and content of your RSS feed to make it more user-friendly and accessible.
Why is my CSS code not validating?
There could be several reasons why your CSS code is not validating. You might be using outdated or deprecated CSS properties, or there could be syntax errors in your code. The CSS validator will highlight these errors and provide suggestions for fixing them. It’s also worth noting that some CSS features are not yet fully standardized, so they might not validate even though they work in most modern browsers.
Can I use CSS Portal’s validator for large CSS files?
Yes, you can use CSS Portal’s validator for large CSS files. However, keep in mind that validating large CSS files can take longer and may require more computational resources. If you’re working with very large CSS files, you might want to consider splitting them into smaller, more manageable chunks.
What does the :checked pseudo-class do in CSS?
The :checked pseudo-class in CSS is used to select and style checkboxes, radio buttons, or option elements that are currently selected or checked by the user. This can be useful for enhancing the user experience by providing visual feedback on the user’s selections.
How can I fix HTML validation errors?
Fixing HTML validation errors typically involves correcting any syntax errors, removing or replacing deprecated elements, and ensuring your HTML code adheres to the latest HTML standards. The HTML validator will highlight these errors and provide suggestions for fixing them.
Why should I validate my web documents?
Validating your web documents helps to ensure they are accessible, functional, and optimized for search engines. It can also help you identify and fix any coding errors that could affect your site’s performance or functionality.
Can I validate my HTML and CSS code offline?
Yes, there are several tools available that allow you to validate your HTML and CSS code offline. These tools work by downloading the W3C’s validation services to your local machine, allowing you to validate your code without an internet connection. However, keep in mind that these tools may not always be up-to-date with the latest web standards.
Published in
·AngularJS·App Development·Mobile·Mobile Web Development·Tools & Libraries·April 11, 2017