How to Force Windows to Delete Files or Folders Using CMD

Sometimes, for whatever reason, Windows will become convinced a given file or folder is in use by a program and prevent it from being deleted, moved or renamed. This locking up of files is incredibly frustrating, especially when you know the file is not, in fact, being used. In this article, we’ll outline how to get around that issue and manually delete files and folders.
Key Takeaways
- To force delete a file in Windows, select the file or folder and press Shift + Delete. This method bypasses the Recycle Bin and permanently deletes the file.
- The Windows Command Prompt (CMD) can be used for advanced file deletion. The ‘del’ command can be used to delete files, while the ‘rmdir’ command can be used to delete folders. Both commands permanently delete files and folders without sending them to the Recycle Bin.
- When using the ‘del’ or ‘rmdir’ commands, exercise caution as these commands will permanently delete files and folders. It’s recommended to double-check the files or folders you’re deleting to avoid accidental data loss.
1. Force delete using Shift + Delete
Perhaps the simplest way to force delete a file in Windows is to use the keyboard shortcut. Select the file or folder you wish to delete, then press Shift + Delete. Note that this deletes files permanently; it won’t be placed in the Recycle Bin.
If that doesn’t work, you can try using the Command Prompt, which offers advanced deletion commands.
2. Force delete files using the Command Prompt (cmd)
The Windows Command Prompt, often simply referred to as “Command Prompt” or “CMD,” is a command-line interpreter application available in Microsoft Windows. It provides a text-based interface for users to interact with the operating system and execute various commands to perform tasks, manage files and directories, configure system settings, and more. In more recent versions of Windows, such as Windows 10 and beyond, Microsoft introduced the Windows Terminal, which is an improved command-line environment that supports multiple command-line interfaces, including Command Prompt, PowerShell, and Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). This provides users with more options and a better overall command-line experience. Check out our comprehensive guide to Windows Terminal.
We can use cmd to forcibly remove the files that we want to delete using the del (short for delete) command.
Open Command Prompt
First, open the command prompt. To do this, start by opening the Start menu (Windows key), typing run, and hitting Enter. In the dialogue that appears, type cmd and hit Enter again, and you’ll see the command prompt, as shown in the screenshot below:
Use the del Command to force delete a file
With the command prompt open, enter del /f filename, where filename is the name of the file or files (you can specify multiple files using commas) you want to delete. Microsoft’s documentation describes more details on advanced deletion methods using this command.
With the command prompt window open, enter the following command: del /f filename, where filename is the name of the file or files (you can specify multiple files using commas) you want to delete and then hit enter. The /f forces deletion of read-only files. Microsoft’s documentation has more detail on advanced deletion methods using this command.
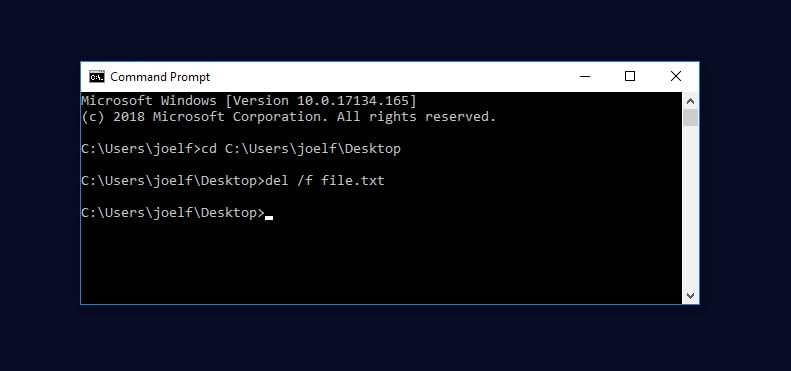
Note that to delete the file you’ll need to either include the full path of the file or first navigate to the folder/directory that the file is in. So if you had a file that you wanted to delete named file.txt located in a folder named examplefolder, you could either use the following command with full path:
del /f C:\examplefolder\file.txt
Or you can use the cd command to navigate to the folder first:
cd C:\examplefolder
And then delete the file using the following command:
del /f file.txt
See the image below for an example of this method:
It’s possible to delete multiple files using the del command by separating the filenames with a space, like this:
del /f file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt
Exercise caution when using the del command, as it will permanently delete the file—it is not moved to the Reycyle Bin!
Force delete folders using rmdir command
Sometimes Windows will prevent you from deleting a folder, especially if they contain files that are in use or locked. To force delete folders in Windows, you can use the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
Open Command Prompt as administrator
Press Win + X and select “Command Prompt (Admin)” or “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” to open a Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
Navigate to the Directory
Use the cd command to navigate to the directory containing the files you want to delete are located. For example:
cd C:\containingfolder
Force delete the folder with rmdir
Use the rmdir command with the /s (remove directory) and /q (quiet) options to delete the folder and its contents. For example, to delete a folder named examplefolder:
rmdir /s /q examplefolder
Again, please exercise a great deal of caution when using the /s and /q options when deleting folders, as they will forcibly delete the entire folder without the possibility of recovery. These files are not moved to the Reycyle Bin! Be sure to double-check the folder you’re deleting to avoid accidental data loss.
Microsoft has more guidance on how to use rmdir here.
There you have it, some very simple methods for fixing a stubborn issue!
FAQs About Force Delete via CMD in Windows
How do I force delete file from CMD?
Navigate to the appropriate folder using the cd command in the command prompt. Then type the following:del /f file.tx
And then press Enter.
What is the del command used for?
The del command is used to delete files and directories from the file system. The term “del” is short for “delete.” It is executed through the Command Prompt or PowerShell interface.
How do I force delete an open file?
Force deleting an open file in Windows can be a bit trickier, as Windows will normally prevent you from deleting files that are currently in use by an application or the operating system. The easiest and probably safest way is to close the application, or restart your computer before attempting to delete the file. However, you can try using the Command Prompt with administrative privileges to force delete a file.
Press Windows + X and select “Command Prompt (Admin)” or “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” to open a Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
Use the del command with the /f (force) and /q (quiet) options to delete the file. For example:del /f /q "C:\examplefolder\file.txt"
Be careful using this method as it can lead to data loss!
How to force delete without prompt in CMD?
If you want to force delete files or directories without receiving confirmation prompts, you can use the /q (quiet mode) option along with the del or rmdir command.
Does the del command permanently delete files?
Yes, the del command in Windows does permanently delete files from the file system. Once you use the del command to delete a file, that file is not moved to the Recycle Bin or any other kind of temporary storage. Instead, it is immediately and permanently removed.
What is the difference between del and erase commands?
del and erase are essentially the same command with different names. The erase command is an older command that originates from MS-DOS operating system, while the del command is a more commonly used and recognized command in modern versions of Windows.
Adam is SitePoint's head of newsletters, who mainly writes Versioning, a daily newsletter covering everything new and interesting in the world of web development. He has a beard and will talk to you about beer and Star Wars, if you let him.



