The Joys of Block Scoping with ES6
Key Takeaways
- ES6 introduces two new keywords for variable declaration, ‘let’ and ‘const’, which allow for block scoping in JavaScript, a feature previously missing and a common source of confusion for developers.
- let’ allows developers to scope variables at the block level (the nearest curly brackets), while ‘const’ is used for values that won’t need to be reassigned during a program’s execution.
- The use of ‘let’ and ‘const’ addresses several challenges associated with the ‘var’ keyword, including confusing scoping, global vs. local confusion, confusing workaround patterns, and misconceptions about hoisting.
- There is ongoing debate in the JavaScript community about when to use ‘const’ vs. ‘let’. Some suggest using ‘let’ in place of ‘var’, while others advocate for defaulting to ‘const’ instead of ‘let’, arguing that it makes the code usage clearer.
Brendan Eich invented JavaScript in 10 days around May 6-15 in 1995. The language, originally called Mocha, started as a simple client-side scripting language. O’Reilly’s history on the language details the context at the time the language was invented:
Eich eventually decided that a loosely-typed scripting language suited the environment and audience, namely the few thousand web designers and developers who needed to be able to tie into page elements (such as forms, or frames, or images) without a bytecode compiler or knowledge of object-oriented software design.
JavaScript was born in a time when the web was very different but would eventually become one of the most ubiquitous programming languages in use. Few could have predicted how popular it would become. Naturally, then, JavaScript has some design flaws that have frustrated and confused developers since its inception.
One of the common complaints has been Javascript’s lack of block scope. Unlike other popular languages like C or Java, blocks ({...}) in JavaScript (pre-ES6) do not have scope. Variables in JavaScript are scoped to their nearest parent function or globally if there is no function present.
When asked why JavaScript has no block scopes, Brendan Eich’s answer is pretty straightforward: there wasn’t enough time to add block scopes.
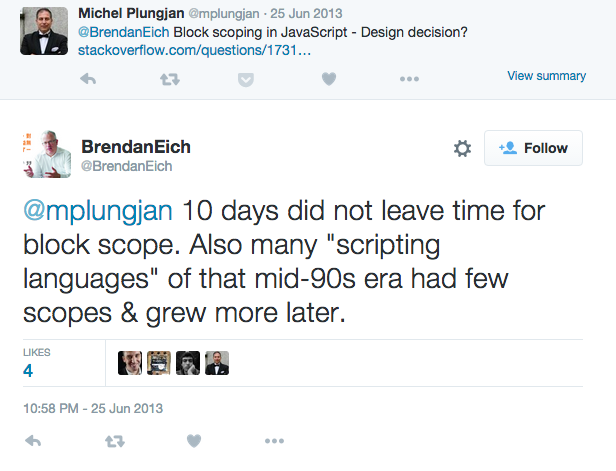
Thankfully, JavaScript descended from C/C++/Java, and was future-proofed for adding block scoping later as Eich explains in this series of tweets.
And now, finally, ECMAScript 6 (ES6) is here and among many things, it gives us block scoping via the two new ES6 variable keywords, let and const. Support for let/const is still limited to Edge, Chrome, and Firefox but more browsers will likely support it soon.
This post will explain why const and let are helpful and how they are used.

source: http://www.cs.uni.edu/~wallingf/blog/archives/monthly/2012-10.html
The Challenges of Using var
Before introducing const and let, it’s worth discussing why they are helpful or necessary in the first place. Var has been the only keyword for variables in JavaScript up until now but it has several drawbacks.
Var scoping is confusing for devs from other languages
The scope of var is confusing for developers coming from other languages. It’s quite easy for them to unintentionally cause bugs in code that uses if blocks or for loops. Variable declaration in ES5 and below doesn’t work in the way they would expect. Given JavaScript’s popularity, developers from other languages sometimes have to write JavaScript, and therefore variable scoping, which is easier to understand, would be helpful for them.
Global vs. local confusion with var
When writing JS using var, it’s difficult to immediately discern which variables are scoped locally vs. globally. It’s very easy to accidentally create a variable on the global object in JavaScript. This generally doesn’t affect simple demo apps but can cause problems for enterprise level applications as team members accidentally obliterate each other’s variables.
Confusing workaround patterns
The lack of clear global vs. local scope differentiation in JavaScript has forced developers to come up with patterns like the IIFE (Immediately Invoked Function Expression). This is an awkward workaround to the lack of block scope. It’s also a way to avoid attaching var-declared variables to the global object.
(function(){
// code here
}());
If you’re not a seasoned Javascript developer, this pattern makes little sense. What is going on here? What are all those parentheses? Why doesn’t that function have a name? Block scoping should lessen the need for workaround design patterns like this.
Misconceptions about hoisting
Another challenge of var is that it doesn’t work in the way most developers think it does. The JavaScript interpreter make two passes on a section of JavaScript code. The first pass processes variables and function declarations and lifts them to the top (the ‘hoisting’). The second pass processes the function expressions and undeclared variables. This makes for some confusing code if the developer is not keenly aware of how hoisting works. Take this example from developer Ben Cherry’s blog:
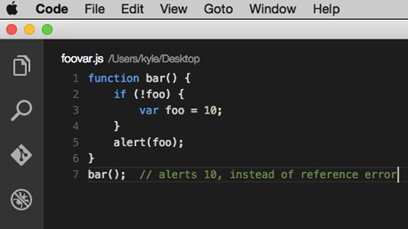
Screenshots in this post are from Visual Studio Code in Mac
code: http://codepen.io/DevelopIntelligenceBoulder/pen/obZYRY?editors=101
In the above example, var foo = 10; is hoisted up to the nearest parent function. That’s why it alerts 10 even though you might think you would get a “ReferenceError: foo is not defined”. The example refactored with let is more intuitive.
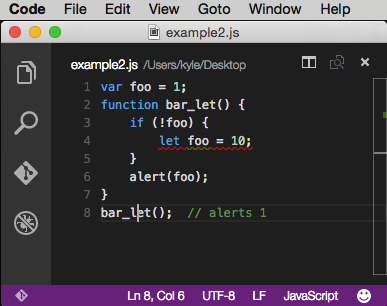
code: http://codepen.io/DevelopIntelligenceBoulder/pen/VvVNpg?editors=101
Using let
The new ES6 keyword let allows developers to scope variables at the block level (the nearest curly brackets). If you’d like to see which browsers support let (and const) follow the Microsoft Edge page for tracking support across ES6 features. You can also check here if your current browser supports let and const.
Here are some examples of let (vs. var) in different types of blocks:
if block example
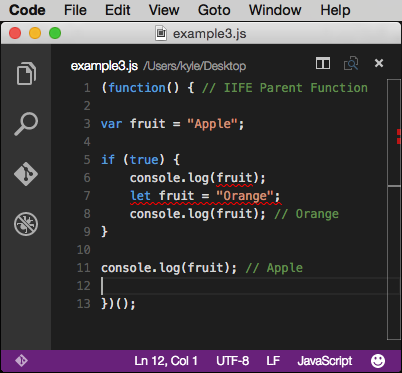
code: http://codepen.io/DevelopIntelligenceBoulder/pen/BoGEoa?editors=101
In the above example, the variable is scoped to the IIFE function when it’s declared with var. Within the if block, a separate fruit variable is declared with let and scoped to the if block.
for loop block example
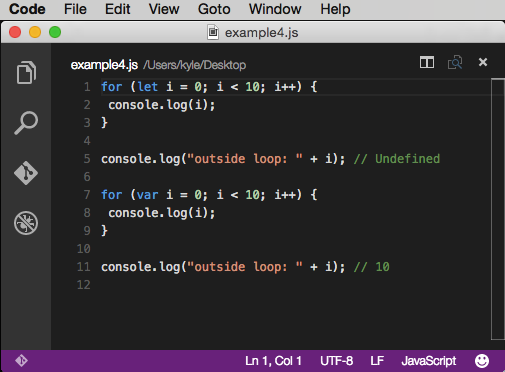
code: http://codepen.io/DevelopIntelligenceBoulder/pen/KdrYdg?editors=101
The for loop example above is a bit more interesting than the if block. By using let in the initialization expression, the i variable is scoped only to the block. By using var, the i will be scoped to the nearest function. The variable will equal 10 outside of the for loop block. This can have consequences such as creating an accidental closure as in examples like this:
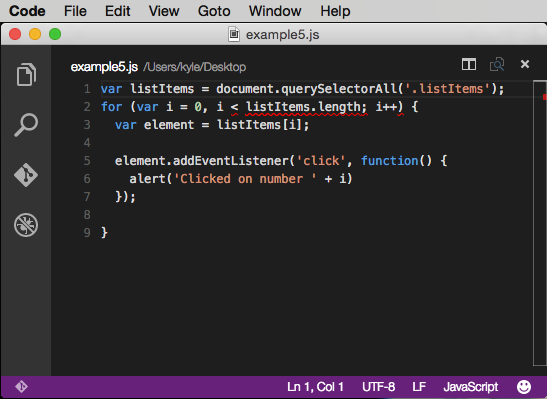
code: http://codepen.io/DevelopIntelligenceBoulder/pen/XmyQXe?editors=101
In this example, the code is meant to register an event listener on a simple list and alert which number was clicked. Instead, it will alert Clicked on Number: 5 for each list item. Wrapping the event listener part in a function would be a common workaround for avoiding the accidental closure.
But instead, refactoring this with let (once it’s fully supported) creates a block scope in the for loop and avoids the accidental closure. It allows the expected iterator to be used within the event listener callback function.
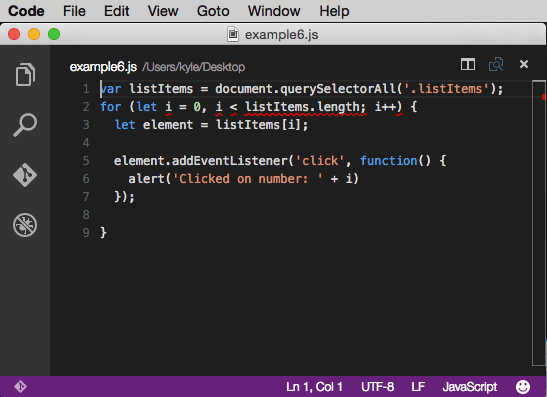
code: http://codepen.io/DevelopIntelligenceBoulder/pen/JYeVGv?editors=101
One caveat with let is that it doesn’t hoist in the same way var does. If you try to use it before it’s been declared, you will get a reference error. This has been termed the Temporal Dead Zone by one developer (the term has gained popularity since).
Using const
Like constants in other languages, const will often be used for values that won’t need to be reassigned in a program’s execution. Strings like API keys or numbers like CANVAS_HEIGHT would be uses cases of const variables that don’t need to be reassigned. Variables declared with const are often written in all caps, but this is a matter of preference.
Const is the other new ES6 keyword for declaring variables. Const works like a constant in other languages in many ways but there are some caveats. Const stands for ‘constant reference’ to a value. The values that const references are not immutable (their properties can be changed). This can be explained by borrowing a metaphor from Eloquent JavaScript (a great beginner’s JS book).
Eloquent Javascript’s author Marijn Haverbeke says that it’s better to think of variables as being tentacles rather than boxes.
They do not contain values; they grasp them — two variables can refer to the same value. A program can access only the values that it still has a hold on. When you need to remember something, you grow a tentacle to hold on to it or you reattach one of your existing tentacles to it.
So with const, you can actually mutate the properties of an object being referenced by the variable. You just can’t change the reference itself. Explained via the above metaphor, the tentacle won’t move or change but what it’s holding onto can. Here are some code examples of const in action:
const PI_VALUE = 3.141592;
const APIKEY = 'aekljefj3442313kalnawef';
const NAMES = [];
NAMES.push("Jim");
console.log(NAMES.length === 1); // true
NAMES = ["Steve", "John"]; // error
If you want a constant to be completely immutable, use object.freeze to make the properties immutable.
When to Use const vs. let
There’s still some debate in the JavaScript community as to when to use const vs. let. Some originally recommended using let in the place of var. Others now call for defaulting to const instead of let.

JavaScript expert Reginald Braithwaite’s tweet above has been echoed by many. Developer Eric Elliot expounds upon the argument for using const before let:
If I don’t need to reassign,
constis my default choice overletbecause I want the usage to be as clear as possible in the code.
constis a signal that the variable won’t be reassigned.
letis a signal that the variable may be reassigned, such as a counter in a loop, or a value swap in an algorithm. It also signals that the variable will be used only in the block it’s defined in, which is not always the entire containing function.
varis now the weakest signal available.
Kyle Simpson (author of You Don’t Know JS) wrote some counterarguments to the enthusiasm around “let is the new var,” suggesting that the implicit nature of let declarations can cause problems in JS code. Furthermore, there are cases when var is still useful:
letimproves scoping options in JS, not replaces.varis still a useful signal for variables that are used throughout the function. Having both, and using both, means scoping intent is clearer to understand and maintain and enforce. That’s a big win!
Simpson believes that let is the companion to var and that it shouldn’t be used to replace all var statements.
It’s still to be determined how this debate will shake out.
Summary
Once they are supported by more browsers, const and let will allow for block scoping variables in JavaScript, rendering patterns like IIFE less necessary. Developers from other languages will likely have an easier time understanding JavaScript scoping. Developer Aaron Frost put it, cheekily, “Using LET and CONST instead of VAR will have an odd side-effect, where your code will execute at runtime just as it appears at development time.”
More Hands-on with Web Development
This article is part of the web development series from Microsoft and DevelopIntelligence on practical JavaScript learning, open source projects, and interoperability best practices including Microsoft Edge browser and the new EdgeHTML rendering engine. DevelopIntelligence offers instructor-led JavaScript Training, AngularJS Training and other Web Development Training for technical teams and organizations.
We encourage you to test across browsers and devices including Microsoft Edge – the default browser for Windows 10 – with free tools on dev.microsoftedge.com:
- Scan your site for out-of-date libraries, layout issues, and accessibility
- Download free virtual machines for Mac, Linux, and Windows
- Check Web Platform status across browsers including the Microsoft Edge roadmap
- Remotely test for Microsoft Edge on your own device
More in-depth learning from our engineers and evangelists:
- Interoperability best practices (series):
- Coding Lab on GitHub: Cross-browser testing and best practices
- Woah, I can test Edge & IE on a Mac & Linux! (from Rey Bango)
- Advancing JavaScript without Breaking the Web (from Christian Heilmann)
- Unleash 3D rendering with WebGL (from David Catuhe)
- Hosted web apps and web platform innovations (from Kiril Seksenov)
Our community open source projects:
- vorlon.JS (cross-device remote JavaScript testing)
- manifoldJS (deploy cross-platform hosted web apps)
- babylonJS (3D graphics made easy)
More free tools and back-end web dev stuff:
- Visual Studio Code (lightweight code-editor for Mac, Linux, or Windows)
- Visual Studio Dev Essentials (free, subscription-based training and cloud benefits)
- Code with node.JS with trial on Azure Cloud
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Block Scoping in ES6
What is the difference between block scope and function scope in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, the scope of a variable defines its accessibility or visibility in the code. Function scope means that a variable is accessible within the function it is declared in, while block scope means that a variable is accessible within the nearest set of curly braces (block of code) it is declared in. The introduction of block scope in ES6 with the ‘let’ and ‘const’ keywords provides more control over variable visibility and can help prevent errors due to variable hoisting and overwriting.
How does block scoping work in ES6?
Block scoping in ES6 works by limiting the visibility of a variable to the block, statement, or expression where it’s defined. This is achieved using the ‘let’ and ‘const’ keywords. When a variable is declared with ‘let’ or ‘const’ inside a block of code (enclosed by curly braces), it can only be accessed within that block. This is different from ‘var’, which is function-scoped and can be accessed outside the block it’s declared in.
What is variable hoisting and how does block scoping help prevent it?
Variable hoisting is a behavior in JavaScript where variable and function declarations are moved to the top of their containing scope during the compile phase, before the code has been executed. This can lead to unexpected results and bugs. Block scoping helps prevent issues related to hoisting because variables declared with ‘let’ and ‘const’ are not hoisted to the top of the block. They are not initialized until their definition is evaluated in the code, preventing access before declaration.
Can I use block scoping with ‘var’ in ES6?
No, you cannot use block scoping with ‘var’ in ES6. The ‘var’ keyword in JavaScript is function-scoped, not block-scoped. This means that if you declare a variable with ‘var’ inside a block, it can be accessed outside that block, which is not the case with ‘let’ and ‘const’.
What is the difference between ‘let’ and ‘const’ in block scoping?
Both ‘let’ and ‘const’ provide block scoping in ES6, but they are used differently. ‘Let’ is used when you want to declare a variable that can be reassigned later in the code. On the other hand, ‘const’ is used when you want to declare a variable that cannot be reassigned after its initial assignment. It’s important to note that ‘const’ doesn’t make the variable itself immutable, just its assignment.
How does block scoping affect closures in JavaScript?
Block scoping can affect closures in JavaScript by providing more predictable behavior. In a closure, an inner function has access to the outer function’s variables. If the outer function’s variables are block-scoped, they retain their values when the inner function is called, even if they’re called outside the block they were declared in. This can make the code easier to understand and debug.
Can I use block scoping in a ‘for’ loop?
Yes, you can use block scoping in a ‘for’ loop in ES6. When you declare a variable with ‘let’ in the initialization of a ‘for’ loop, that variable is block-scoped to the loop. This means it’s re-declared for each iteration, which can be useful if you’re creating functions within the loop and want each one to have its own copy of the variable.
What happens if I declare the same variable with ‘let’ or ‘const’ in the same scope?
If you declare the same variable with ‘let’ or ‘const’ in the same scope in ES6, you will get a syntax error. This is because ‘let’ and ‘const’ do not allow you to redeclare the same variable in the same scope, unlike ‘var’. This can help prevent bugs caused by accidental variable redeclaration.
Can I use block scoping in ES5 or earlier versions of JavaScript?
No, block scoping with ‘let’ and ‘const’ is not available in ES5 or earlier versions of JavaScript. These keywords were introduced in ES6 to provide more control over variable scoping. In ES5 and earlier, you can only use ‘var’ for variable declaration, which is function-scoped.
How does block scoping improve code readability and maintainability?
Block scoping can improve code readability and maintainability by limiting the visibility of variables to the blocks they are declared in. This can make it easier to understand the code because you don’t have to look outside the current block to understand what a variable is doing. It can also help prevent bugs caused by variable hoisting and overwriting, making the code more maintainable.
Kyle is a Technical Instructor at DevelopIntelligence. He spends his time reading, coding, biking, and exploring live music in Denver. He enjoys trying to make technical concepts more approachable and likes tinkering with music and mapping APIs.

Published in
·CMS & Frameworks·Development Environment·Frameworks·Laravel·News & Opinion·PHP·Standards·Symfony·Web·March 3, 2017