How Many of Your Users Need Accessible Websites?
Key Takeaways
- The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) were created to ensure equal access and opportunity for people with disabilities, including those with visual and hearing impairments.
- There are 285 million people worldwide with some disability that prevents them from reading all content on a website, and 39 million of those are blind. Additionally, there are 360 million people suffering from hearing loss worldwide. These statistics underline the importance of creating accessible web content.
- Web accessibility is not just about catering to those with permanent disabilities. It also benefits people who may have temporary disabilities, are not fluent in English, or are unable to use a keyboard or mouse. Making websites accessible to all increases website traffic and ultimately leads to a more successful website.
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) came into existence in order to provide equal access and equal opportunity to people with disabilities. If the Web is accessible, many people with disabilities can communicate and interact with content much more easily.
In this article I will list some statistics released by the World Health Organization (WHO) and other known sources. I hope this post will help to create awareness on the importance of creating content for those using assistive technology, including blind as well as hearing impaired people.
Note: Some of the data presented in this article in images is not accessible. The images are merely to demonstrate some of the statistics in another format. All of the images have source links where the data can be found in more accessible formats (e.g. PDF).
Understanding Why People Have Disabilities
Before getting into the stats, let’s first briefly look at some causes behind disabilities:
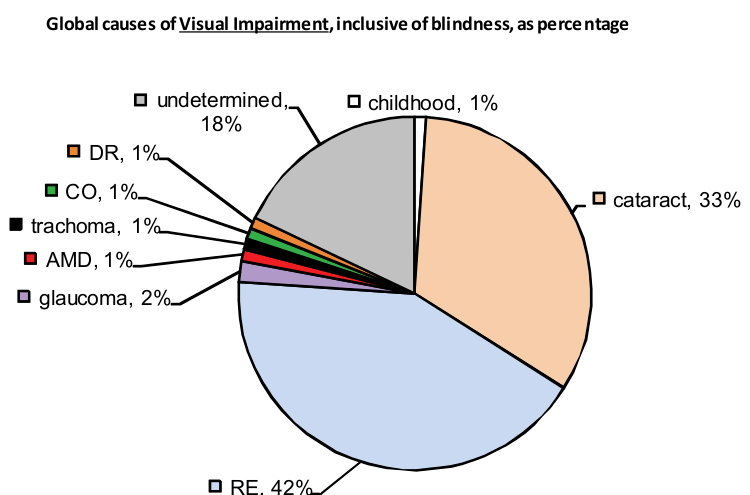
- Blindness is caused, among other things, by glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosis, onchocerciasi, and corneal opacification. These diseases often limit a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks and affects their quality of life. Naturally, this will also affect their ability to access web content.
- Hearing loss may be inherited, caused by maternal rubella or complications at birth, certain infectious diseases such as chronic ear infections, exposure to excessive noise, ageing, and so on. The same quality of life factors are at play here, and specifically this will affect how they access audio content on web pages.
We don’t need an extensive discussion of causes here, so that should suffice to get a general understanding. Let’s consider the stats now.
Worldwide Blindness Statistics:
According to WHO, there are 285 million people worldwide who, due to some disability (i.e. they are suffering with low vision), cannot read all content on a website. 39 million of those people are blind and cannot access any of the content via sight.
Additionally, there are 360 million people suffering from hearing loss worldwide.
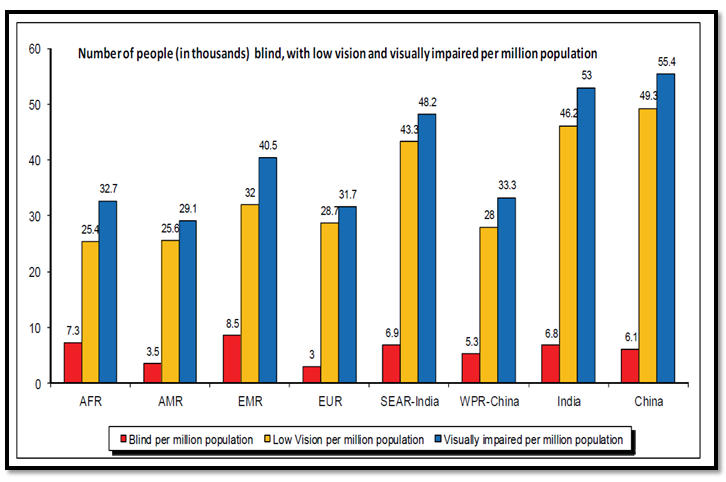
Here are some further statistics:
- Approximately one-third of persons over 65 years of age are affected by disabling hearing loss.
- About 90% of the world’s visually impaired live in developing countries.
- 82% of people living with blindness are aged 50 and above.
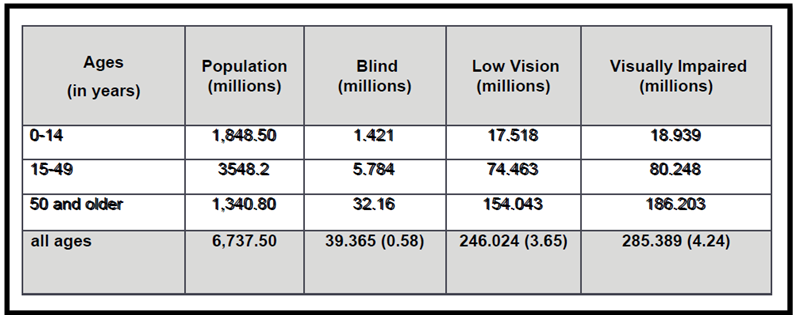
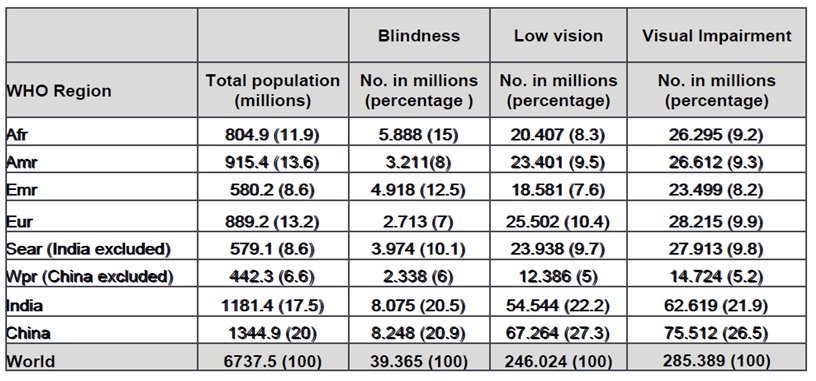
UK Blindness Statistics (FightForSight)
Here are some facts from thee FightForSight report, a study done in the UK:
- 2 million people in the UK are living with sight loss. These figures are expected to rise to over 2,250,000 in 2020 and nearly four million in 2050.
- There are 360,000 people registered as blind or partially sighted in the UK who have irreversible sight loss.
- An estimated 25,000 children in the UK are blind or partially sighted.
- Someone in the world goes blind every 5 seconds.
- 50% of sight loss cases cannot be avoided.
Blindness Statistics in India
- India has one the largest blind populations in the world with around 15 million blind people.
- It is said that one out of every three blind people in the world lives in India.
- There are around 2 million blind children in India.
- There are 30,000 new cases of blindness every year.
- Glaucoma is the largest cause of blindness in India, currently affecting more than 4.5 million people.
Some statistics related to Deafness (2012)
Accessibility guidelines are not for blind people only. As mentioned above, there are more than 600 million people suffering from hearing problems, cognitive disabilities, and other hearing-related issues. The figures below show some data from WHO regarding hearing disabilities:
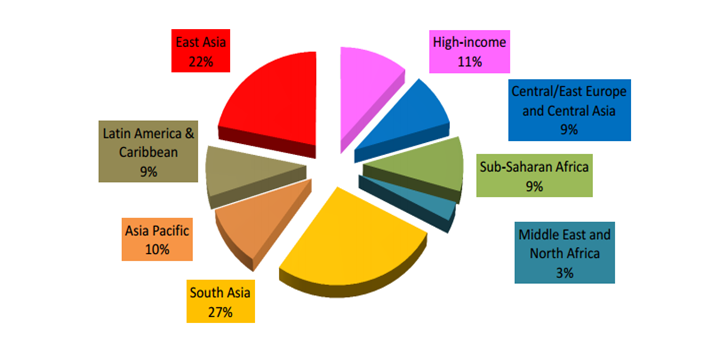
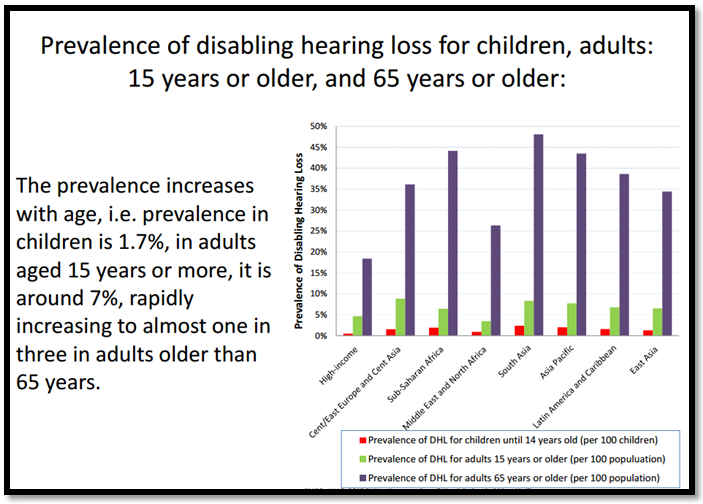
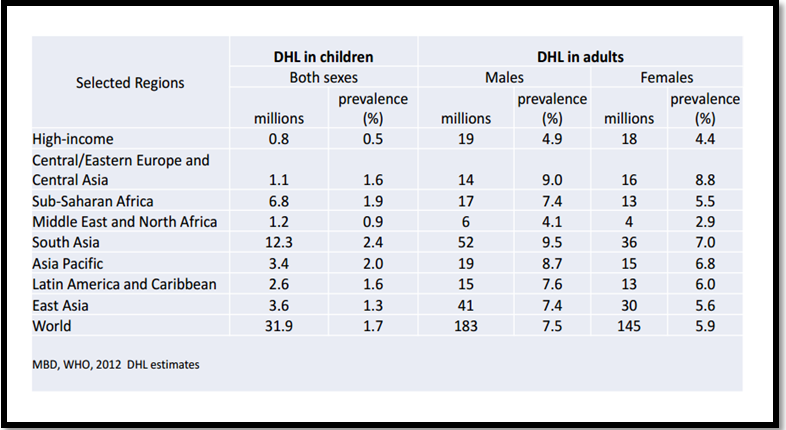
A Social and Legal Issue
If your content is not equally distributed to everyone then this lack of accessibility becomes a social and legal issue. There are some laws that define that services provided should be available to everyone regardless of ability.
The 2010 Equality Act and its predecessor the 1995 Disability Discrimination Act created a legal duty for businesses and organizations to ensure their services are available to everyone regardless of disability.
There is a misconception that the main focus of web accessibility may be people with permanent or long-term disabilities, but accessibility benefits people with or without disabilities. For example, those impacted include:
- People who are not fluent in English.
- People who do not have or are unable to use a keyboard or mouse.
- People with temporary disabilities due to accident or illness.
- Older people.
- New users.
There are a number of initiatives under way all over the world to create awareness about accessibility, the visually impaired, hearing disabled people, and other issues, including Google’s Web accessibility course, Foundation Fighting Blindness, Adobe’s Accessibility Initiatives (PDF), and more.
The Future of Accessibility
There is much to look forward to as many big initiatives are taking relevant steps to spread awareness. There is Google’s Accessible Web Search for visually impaired people, Foundation Fighting Blindness, various initiatives by World Health Initiatives are just a few.
I personally know more than 50 people suffering from incurable eye diseases with low vision from India, USA, Nepal, South Africa, etc. I also have had conversations with more than 20 designers and developers who have developed interactive websites, but still don’t know the importance of accessible websites.
I look forward to users with disabilities having the same ability to access content as everyone else. And if designers and developers need any extra incentive, besides those already mentioned in this article, making a websites equally accessible to all means your website traffic will increase and ultimately this will mean a more successful website.
So how many of your users require accessible content? You won’t know unless you analyze your own visitor data. In the meantime, the stats discussed above should give you a general idea that you can use as a gauge for future projects.
Frequently Asked Questions on Website Accessibility for Visually Impaired Users
Why is website accessibility important for visually impaired users?
Website accessibility is crucial for visually impaired users because it ensures that they can access, understand, and interact with online content. It’s not just about providing equal access to information and services, but also about promoting inclusivity and diversity. When websites are designed and developed with accessibility in mind, they can be used effectively by everyone, regardless of their physical abilities or disabilities. This includes people with visual impairments, who may rely on assistive technologies like screen readers to navigate the web.
What are the common barriers faced by visually impaired users on the web?
Visually impaired users often encounter several barriers when navigating the web. These include lack of text alternatives for images, poor color contrast, non-responsive design, and lack of keyboard accessibility. Additionally, complex layouts, small text sizes, and the absence of skip navigation links can make it difficult for visually impaired users to understand and interact with web content.
How can websites be made more accessible for visually impaired users?
Websites can be made more accessible for visually impaired users by following the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). These guidelines recommend providing text alternatives for non-text content, using sufficient color contrast, ensuring that all functionality is available from a keyboard, and designing content in a way that it can be presented in different ways without losing information or structure. Additionally, websites should be tested with assistive technologies to ensure they are fully accessible.
What is the role of assistive technologies in web accessibility?
Assistive technologies play a crucial role in web accessibility. They help visually impaired users perceive, understand, and interact with web content. Examples of assistive technologies include screen readers, which convert text into speech, and screen magnifiers, which enlarge text and images on the screen. By ensuring that websites are compatible with these technologies, we can make the web more accessible for visually impaired users.
What are the legal requirements for website accessibility?
The legal requirements for website accessibility vary by country. In the United States, for example, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires that all websites be accessible to people with disabilities. This means that websites must be designed and developed in a way that they can be used effectively by everyone, including visually impaired users. Non-compliance with these requirements can lead to legal action and penalties.
How does website accessibility benefit businesses?
Website accessibility benefits businesses in several ways. It expands their customer base, improves their SEO performance, enhances their brand reputation, and reduces the risk of legal issues. By making their websites accessible, businesses can reach a wider audience, including the millions of people worldwide who have visual impairments.
How can I test my website for accessibility?
There are several tools and services available that can help you test your website for accessibility. These include automated testing tools, manual testing tools, and user testing services. Automated testing tools can quickly identify common accessibility issues, while manual testing and user testing can provide more detailed insights into the user experience.
What is the impact of website accessibility on SEO?
Website accessibility can have a positive impact on SEO. Many accessibility practices, such as providing alt text for images and using descriptive link text, also improve SEO. Additionally, search engines favor websites that provide a good user experience, and accessibility is a key part of that.
How can I learn more about website accessibility?
There are many resources available for learning about website accessibility. These include online courses, webinars, blogs, and guides. Additionally, organizations like the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) provide comprehensive information and guidelines on web accessibility.
What is the future of website accessibility?
The future of website accessibility looks promising. With increasing awareness about the importance of accessibility and advancements in technology, more and more websites are becoming accessible. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards inclusive design, which considers the diverse needs and abilities of all users from the outset. This not only makes websites more accessible, but also improves the overall user experience.
Amit Diwan is a founder at Studyopedia, who has taught more than a million engineers and professionals on the following technologies: Python, Java, Android, WordPress, Drupal, Magento, JavaScript, jQuery, HTML5, Bootstrap 4, etc.
Published in
·Accessibility·Design·Design & UX·Freelancing·Illustration·Sketch·Software·UI Design·Usability·UX·Web·March 23, 2016
Published in
·Agile Development·Blogs·Business·Copywriting·Entrepreneur·Entrepreneurship·Entrepreneurship·Freelancing·Marketing·Testing·August 26, 2015
