How to Contribute to Open Source TypeScript Projects

Key Takeaways
- Assess your skill level in TypeScript before diving into open source contribution. The author suggests three levels: new to TypeScript, comfortable with TypeScript, and ready for TypeScript challenges. Each level has different types of contributions suitable for it.
- Use platforms like GitHub, Twitter, and Discord to find opportunities for contributing to open source TypeScript projects. GitHub has numerous open source projects, Twitter can help you connect with the TypeScript community, and Discord allows you to interact directly with other TypeScript enthusiasts.
- Contribute according to your skill level. Beginners can update documentation or create links to the TypeScript playground for examples. Intermediate users can fix bugs or type errors, add small features, and contribute to cheat sheets. Advanced users can help maintain typings in DefinitelyTyped, write advanced tutorials, or contribute to the TypeScript compiler itself.
- Contributing to open source TypeScript projects not only helps the community but also allows you to enhance your TypeScript skills. It’s important to choose projects that align with your current skill level and where you aspire to be.
If you think of the ideas of open source applied to information in an encyclopedia, you get to Wikipedia – lots and lots of small contributions that bubble up to something that’s meaningful. – Matt Mullenweg
One of my favorite aspects of open source is the fact that anyone can contribute! It’s like “productive volunteering” (if you’ll humor me). It’s a fantastic way to build something bigger than you, give back to the community, and level up your skills.
In this article, we’re going to talk about practical ways for you to get involved in open source TypeScript projects. We’ll first cover assessing your level then jump into how you can find opportunities.
Assessing Your Level
Before you get started contributing to open source, you want to find your comfort level. Where are you at skill-wise? What level of complexity are you wanting to solve? How much time do you want to spend? These are important questions to consider before diving in. This information will guide us during the process of finding opportunities.
To simplify things, we will create three levels:
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
In each level, we will provide a description and an example contribution for someone at that level. Let’s take a look.
Level 1: New to TypeScript
The first level in our three-level TypeScript skills assessment is for those who are “new to TypeScript.” You might find yourself here if any of this description resonates with you:
You are new to TypeScript. You feel comfortable enough with JavaScript that you decided to give TypeScript a try. You have looked at the docs briefly. Maybe you’ve gone through a tutorial or two and. Maybe you’ve watched a video about TypeScript on YouTube. “Beginner” feels accurate when labeling your TypeScript skills.
Below are a few examples of things you might contribute to while you are at this level:
- updates to documentation
Level 2: Comfortable with TypeScript
The next level in our system is where I imagine most people self-categorize. Read the description and see if this relates to how you are currently feeling:
You’ve used TypeScript in a few projects. You feel comfortable with TypeScript and understand how to fix general type errors. You’re not an expert when it comes to understanding issues, but you sure know how to find the answer. Maybe you’ve written a handful of interfaces or type aliases. You know a decent number of TypeScript tricks or tips. The compiler isn’t your bestie, but you consider yourselves acquaintances.
At this level, you might feel comfortable contributing in the following ways:
- fixing bugs
- fixing a type error
- making a switch statement exhaustive
- adding small features
- converting
anyto the correct type
- converting
- updating docs with new examples, templates, etc.
- contributing to a cheatsheet
Level 3: Ready for TypeScript Challenges
The last level we’ll have is for people who feel quite comfortable with TypeScript and are ready for a challenge! Take a glance at the description below and see if that’s how you would describe your level:
If someone were keeping score, it would say, “TypeScript 0. You 1”. You feel comfortable with TypeScript. Maybe you’ve converted a JavaScript codebase to TypeScript. Maybe you’ve written a large project from scratch in TypeScript. You’ve figured out how to decipher cryptic TypeScript messages. Maybe others come to you when they need TypeScript help. Maybe you’ve taught others TypeScript and others refer to you as the “TypeScript” person.
A few examples of where you might look to contribute:
- helping maintain typings in DefinitelyTyped
- writing advanced tutorials or documentation for new TypeScript projects
- contributing to TypeScript, the compiler, itself
Finding Opportunities
Now that you have an idea of what level you’re at, it’s time to think about where you should start looking for opportunities. We’ll cover three where you might have luck.
GitHub
Yes, this is clearly the most obvious. You’ll find lots of open source projects on GitHub. However, it can often be overwhelming. Where do you even start?
The best place to start is TypeScript specific organizations and repos. These are organizations with lots of TypeScript repos. Let’s look at a typical search process. Here are the steps you might go through after you’ve found a TypeScript organization or repo using TypeStrong:
- Open repo from organization → fork-ts-checker-webpack-plugin
- Navigate to issues → /issues
- Look for a “help wanted” or “good first issue” type of label
- Now, go to the global issues page → https://github.com/issues
- Filter by org, issue state and label → example
- Sort by least commented → sort:comments-asc
- Find an issue that fits with your level
The reason for sorting by least commented is this helps find issues that have yet to be claimed or worked on. I have used a similar tactic in the past contributing to Rust open source and it worked out well!
The next best place to look after GitHub is Twitter. Why? Well, it’s a great place to share what you’re doing and others might notice. If you mention that you’re actively looking to contribute to TypeScript open source projects, someone may point you in a direction.
This is how I found one of the open source projects I contributed to:
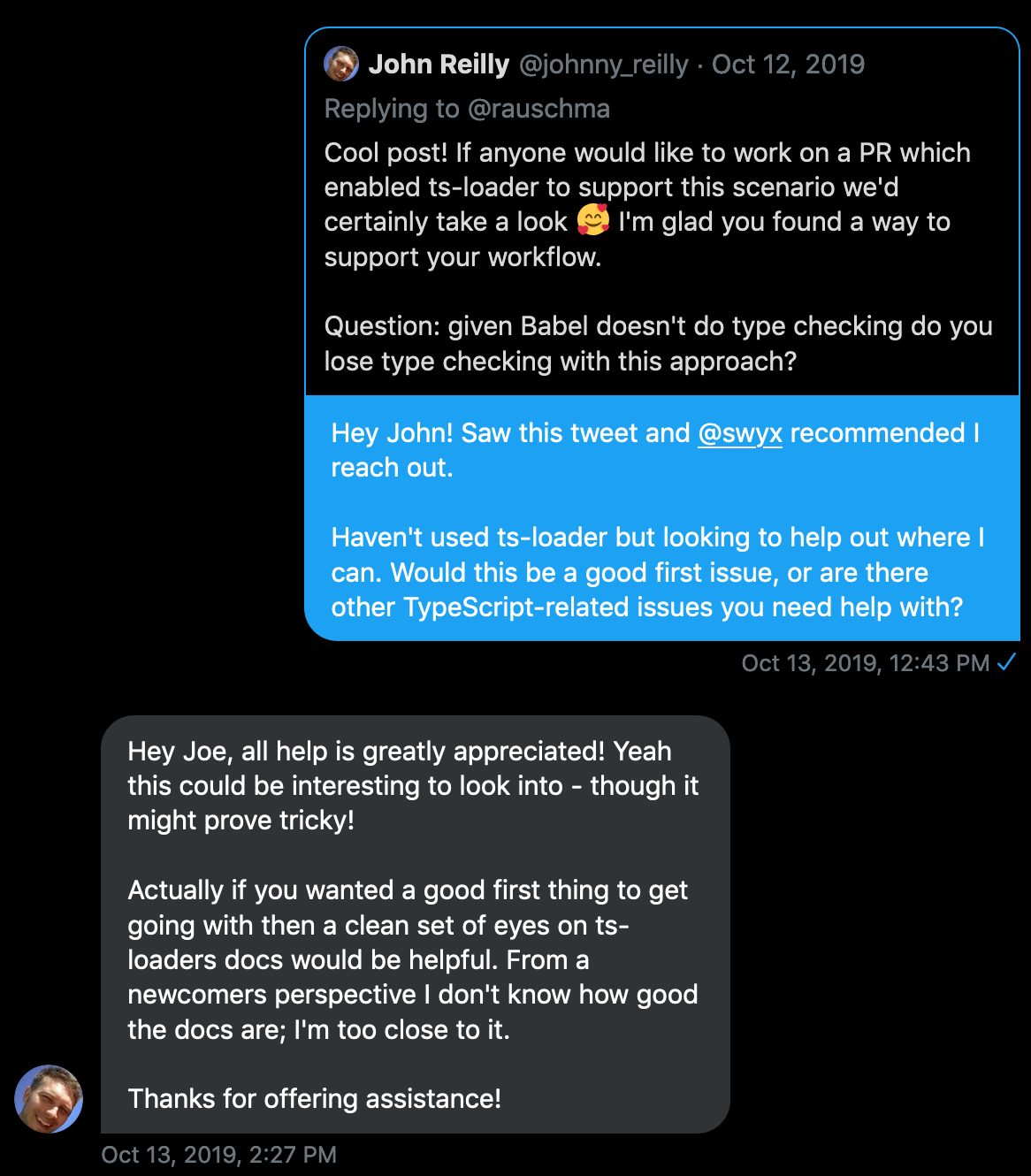
Again, a friend (@swyx) knew I was looking for open-source projects to hone my TypeScript skills and pointed this tweet out to me. That lead to an issue to improve the docs for beginners and three PRs that were merged in.
On a more practical side, here’s what you can do to increase your luck of finding open source TypeScript projects on Twitter:
- Learn in public i.e. share your goals with others
- Follow prominent TypeScript community members (start with the list that @typescript follows)
- Search for tweets mentioning TypeScript
There may be less opportunity on Twitter, but it’s still worth the effort as an additional avenue.
Discord
The TypeScript community has its own Discord server. Here you can mingle with other members and chat about projects, but you could also post about open-source and share what you’re looking for! I haven’t personally tried this, but I would if I were looking.
It may be hit or miss, but I am almost certain someone will know of an issue or be willing to help find one that fits your skill level.
Summary
Contributing to TypeScript open source gives you the opportunity to collaborate with others on projects used by the community. It also provides a way to level up your skills. It is a win-win for both groups.
Remember to understand where your skill level is at and where you want to be when choosing which projects to tackle. Take advantage of GitHub’s special search syntax, but also don’t neglect Twitter or Discord. Like a good carpenter, know how to use all your tools.
I hope you found this article helpful! If you did, tweet @jsjoeio and let me know!
If you used any of this information to find and contribute to TypeScript open source, let us know in the comments below!
Happy coding!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Open Source TypeScript
What are the benefits of using TypeScript in open-source projects?
TypeScript offers several advantages for open-source projects. Firstly, it provides static typing, which can help catch errors at compile-time rather than at runtime. This can significantly improve the quality of the code and reduce the number of bugs. Secondly, TypeScript supports modern JavaScript features, including classes, modules, and interfaces, which can make the code more readable and maintainable. Lastly, TypeScript has excellent tooling support with IntelliSense, which provides active hints as a code is added.
How can I contribute to TypeScript open-source projects?
Contributing to TypeScript open-source projects can be a rewarding experience, both in terms of learning and giving back to the community. You can start by finding a project that interests you on platforms like GitHub. Once you’ve found a project, you can contribute in several ways: fixing bugs, adding new features, improving documentation, and more. Remember to follow the project’s contribution guidelines and respect the code of conduct.
What are some popular open-source projects that use TypeScript?
There are many popular open-source projects that use TypeScript. Some of them include Angular, a platform for building web applications; VS Code, a code editor; Deno, a secure runtime for JavaScript and TypeScript; and NestJS, a framework for building efficient and scalable server-side applications.
How can I start my own TypeScript open-source project?
Starting your own TypeScript open-source project can be an exciting endeavor. You can start by identifying a problem that you want to solve or a concept that you want to explore. Once you have a clear idea, you can start writing your code using TypeScript. Make sure to write clear documentation and provide a comprehensive README file to help others understand your project. You can then publish your project on platforms like GitHub and invite others to contribute.
What are the best practices for using TypeScript in open-source projects?
There are several best practices for using TypeScript in open-source projects. These include using strict mode to catch potential errors at compile-time, leveraging TypeScript’s powerful type system to make the code more readable and maintainable, using interfaces to enforce contract for classes, and using modules to organize code. Additionally, it’s important to keep up with the latest TypeScript versions and features.
How can I learn TypeScript for contributing to open-source projects?
There are many resources available to learn TypeScript. You can start with the official TypeScript documentation, which provides a comprehensive guide to the language. There are also many online tutorials and courses available on platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and freeCodeCamp. Additionally, contributing to open-source projects and reading other people’s code can be a great way to learn and practice TypeScript.
Can I use TypeScript with other JavaScript libraries and frameworks?
Yes, TypeScript can be used with most JavaScript libraries and frameworks. TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript, which means that any valid JavaScript code is also valid TypeScript code. Additionally, TypeScript provides definition files (with .d.ts extension) that allow you to use existing JavaScript libraries and frameworks in a TypeScript-friendly way.
What tools can I use to write and compile TypeScript code?
There are several tools available for writing and compiling TypeScript code. The TypeScript compiler (tsc) is the official compiler that you can use to compile your TypeScript code to JavaScript. There are also many code editors that support TypeScript, including VS Code, Atom, and Sublime Text. These editors provide features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking, which can make your coding experience much smoother.
How can I debug TypeScript code?
Debugging TypeScript code is similar to debugging JavaScript code. You can use console.log statements for simple debugging. For more complex debugging, you can use debugging tools provided by your code editor or browser. For example, VS Code provides a powerful debugger that allows you to set breakpoints, step through your code, inspect variables, and more.
How is TypeScript different from JavaScript?
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript, which means it includes all JavaScript features plus some additional features. The main difference is that TypeScript supports static typing, which allows you to specify the types of variables, function parameters, and return values. This can help catch potential errors at compile-time. TypeScript also supports interfaces, generics, and other advanced features that are not available in JavaScript.
Joe Previte is a developer, a teacher and creator of Vim for VSCode. In his spare time, he enjoys creating videos for egghead, writing articles relating to coding and leading an online meditation study group.