How to Grunt and Gulp Your Way to Workflow Automation
This article is part of a web dev series from Microsoft. Thank you for supporting the partners who make SitePoint possible.
When you are new to front-end development and start mastering HTML5, CSS and JavaScript, the obvious next step is to put your hands on tools that most developers use to stay sane in this complex space. You too deserve to have more flexibility and features while writing your CSS sheets by using Less. You too deserve to optimize bandwidth by minifying your JS code. You too deserve to be able to automatically check that your JS code is good using JSHint. You deserve all this good stuff.
So you start to use all these great tools by hand; running more and more command lines manually. Sometimes, you forget to run the Less compiler. Sometimes you forget to run JSHint and a bug is shipped…
And suddenly you find yourself wondering: is there any solution to automate all these tools? How can you create a repeatable workflow to prevent you from doing mistakes?
Obviously a solution exists, and two tools in particular are waiting for you to get started: Gruntand Gulp.
As a newbie using these tools, you are wondering how they work and which one to use, aren’t you? Well perfect then, you are reading the right article!
Key Takeaways
- Utilize Grunt and Gulp to automate repetitive tasks in front-end development such as minifying JavaScript, compiling CSS, and running code checks, enhancing productivity and reducing manual errors.
- Understand the role of Node.js Package Manager (npm) in managing dependencies and facilitating the use of tools like Grunt and Gulp through the creation and manipulation of the `package.json` file.
- Grunt operates on a configuration-based approach, allowing you to declare tasks in a `Gruntfile.js`, making it suitable for straightforward task automation with a vast plugin ecosystem.
- Gulp employs a code-over-configuration strategy using streams, enabling more complex and flexible task automation by chaining functions in a `gulpfile.js`.
- Choose between Grunt and Gulp based on project needs: Grunt for simpler, configuration-driven tasks, and Gulp for more complex scenarios requiring coded tasks and stream handling.
The Sample We’ll Use
I will give you the basis for using Grunt and Gulp using a really simple example that you can download here: http://aka.ms/gruntgulpplugin
It is a simple web site composed of three files:
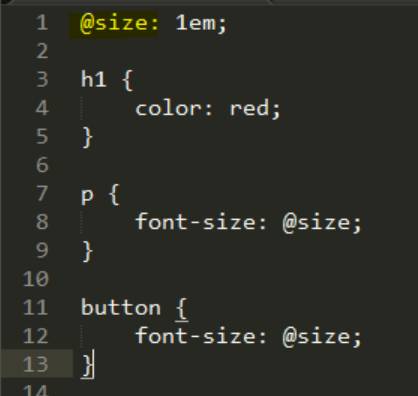
Styles.less define the CSS sheet in a richer manner that what you can do using standard CSS file. In the end we use the Less compiler to create a styles.css file. Using less, we are able for instance to use variables in the css file:
Get more info about Less here: http://lesscss.org/
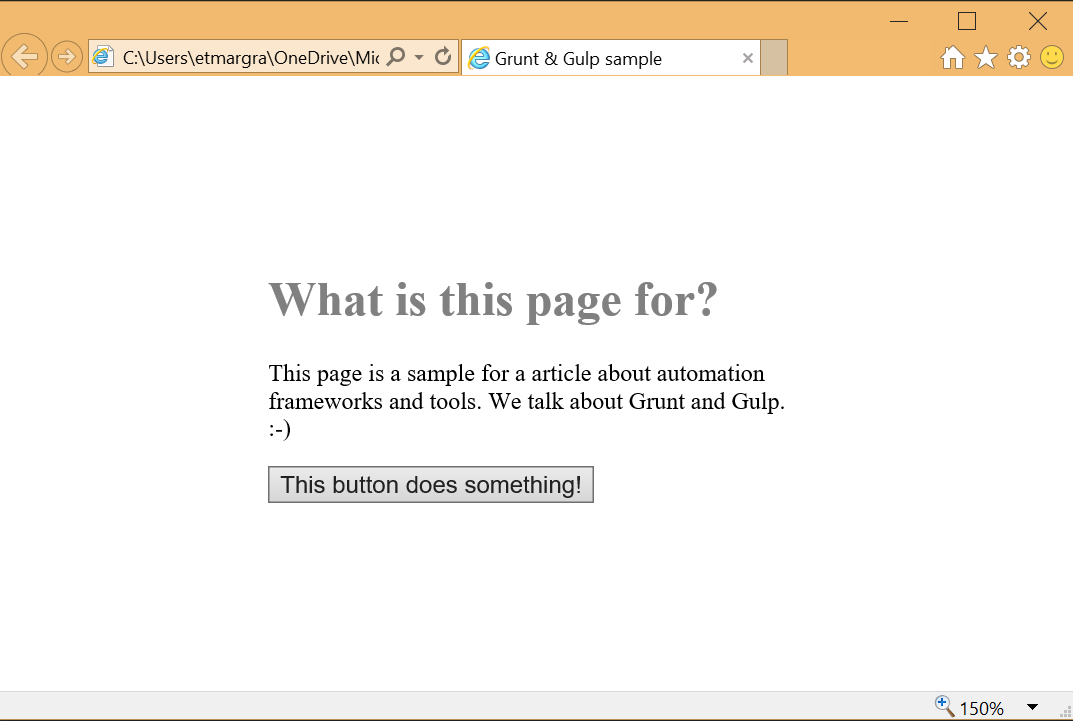
The JavaScript and HTML code are really simple. The page should look like this:
Understanding Node.js Package Manager
You need to understand first how Node.JS Package Manager (npm) works.
Npm is the tool provided with Node.JS. It is used to get tools and frameworks while automatically resolving their dependencies.
For instance, to use less and compile it into a web usable CSS file, you first need to install less using this command:
npm install -g lessNote: To get the npm command line, you have to install nodejs from http://nodejs.org/
Once this is done you can run this command to compile .less files into .css:
lessc styles.less > styles.cssNpm uses a file that it creates and store on the local folder it is working: package.json. This file is using the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format to let npm know which tool and version is installed and the frameworks used by the current project (which is represented by the current folder).
This file is important for Grunt and Gulp because it will contain the list of plugins downloaded and usable in your automation workflow.
To create an empty package.json file you can use the following npm command:
npm initYou will go through some questions that you can answer using the default option, then you will be all set to start.
In this file you will have two kinds of dependencies:
- The ones needed for the execution of your web app / nodejs app
- The ones needed for the development phase (like Less) and which are used to compile / check your code
Npm basically gives you three ways to install packages:
- Globally on your machine using the
–g or-globaloption - For execution purpose, locally on your project folder using no options (only npm install [tools or framework])
- For dev purpose, locally on your project folder using the
--save-devoption
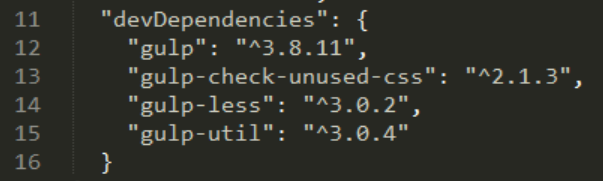
The third one will create a devDependencies section / property inside the package.json file.
Grunt
What is grunt?
Grunt is a pioneer in the JavaScript automation workflow area. There are a lot of known Grunt users like Twitter, jQuery and Modernizr.
The basic principle for Grunt is to give us an easy way to run tasks. A task is a set of code files and configuration files already created for you. You can get new tasks by installing Grunt plugins that you will get using npm. You can find a plugin for pretty much every tool you might use, such as Less and JSHint.
To run Grunt, you have to create a Gruntfile in which you specify which tasks you want to run and the configuration for each of them. Once this is done, you only have to run the grunt command line specifying the task you want to run (default or a specific one) and it will do it automatically.
Now let’s go through a step by step guide to set up all this.
Step 1. Create the package.json file
Use npm to init the file:
npm initYou will have to answer a few questions like the project name and what is the default .js file. You can also choose to create the file manually and setting its content to:
{
"name": "project-name",
"devDependencies": {},
"dependencies": {}
}Step 2. Install Grunt globally and locally
You need to install Grunt globally to get the command line and locally to initialize everything needed for the project.
Run:
npm install -g gruntThen run it locally:
npm install grunt --save-devNote: Do not forget the –dev part for it to be specified as a devDependencie in the package.json file.
Step 3. Create the gruntFile.js
Grunt works using a file named gruntFile.js. This file contains everything needed by Grunt, that is to say:
- Configuration for tasks
- Custom tasks
- Task loading
Grunt expect the file to export a single function which take one parameter named grunt. You will use this object to perform all Grunt related actions.
Here is a minimal gruntfile that only read the package.json file and create a default task which runs nothing.
Note: place the file in the project folder, side by side with the package.json file
module.exports = function(grunt) {
// Project configuration.
grunt.initConfig({
pkg: grunt.file.readJSON('package.json'),
});
// Default task(s).
grunt.registerTask('default', []);
};You can execute it to be sure everything is configured correctly.
To do that, open a command prompt on the project folder and run:
gruntYou should see something like this:

Step 4. Add your first task: JSHint
Now that your Gruntfile is ready, the next step is to add a plugin and use it. All plugins can be found here: http://gruntjs.com/plugins. One of the common tasks performed in a Gruntfile is checking if the JavaScript syntax is correct. To do that, we usually use JSHint.
Let’s add is to your grunt workflow.
If you search for JShint on the grunt plugins page, you will find grunt-contrib-jshint (here) which corresponds to what we need!
In the project folder, run:
npm install grunt-contrib-jshint --save-devOne this is done you have to add it in your Gruntfile.js. There are two simple steps for that:
- Load the plugin
- Configure the task
To load the plugin, use the loadNpmTasks function:
// Load the plugin that provides the "jshint" task
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-contrib-jshint');The configuration is done in the initConfig function where you have to add a new property to the object given in parameter. This have to be the name of the task you want to add and is related to the plugin you use. The best way to know that name and the list of available options for the task is to have a look at the plugin documentation. You will always find a well-documented sample.
For instance, in our sample we want to check all the JavaScript files except the gruntfile.js. We also want to activate a set of rules to check in the JavaScript files like eqeqeq to ensure we use triple equals when needed.
Here is the initConfig function modified:
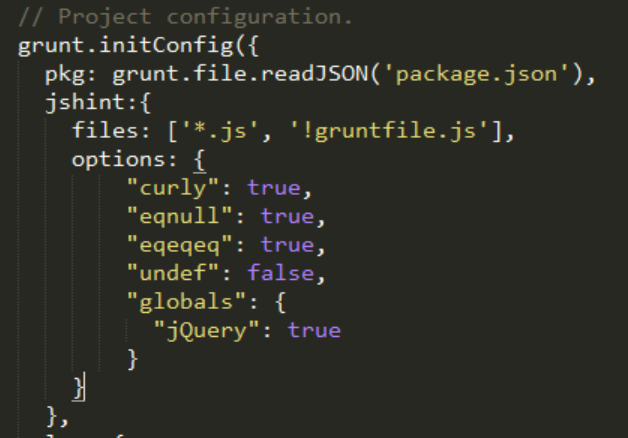
You can run your task by using the following command line (where you specify the task name as a parameter for grunt):
grunt jshintThe result is here:
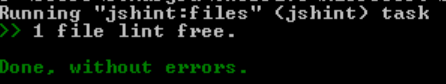
You just have to run that command and it will automatically prompt you for any errors it encounter.
Congratulation, you now have a task automated in your grunt workflow!
Step 5. Add a second task: Less compilation
Your JShint task works well but it is a little bit alone in the workflow. Usually, we are using tools like grunt to run more than one task.
It is really easy to add more of them as you just have to follow the same steps. Let’s say you now want to add the compilation for your less file inside the automated process. If you search in the grunt plugins, you will find a grunt-contrib-less plugin that you can install on your project folder:
npm install grunt-contrib-less --save-devLike for the jshint task, you have to add the configuration:
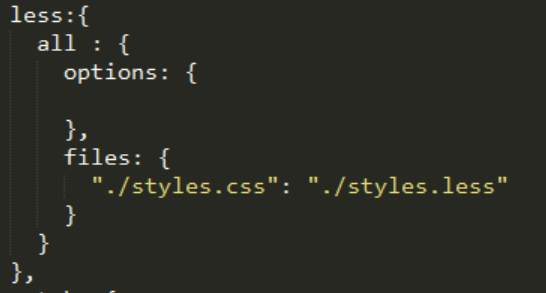
Then, load the task:
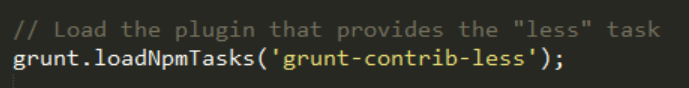
You can now run Grunt and specify the less task: this will launch only less. That is OK but you want to run all the tasks right? That is the role of the default task.
When you just run grunt without specifying any task it will search for a default task and run all the task specified in its array. You can modify it to run less and jshint. Note that to add a group of tasks like default your need to call the registerTask function:
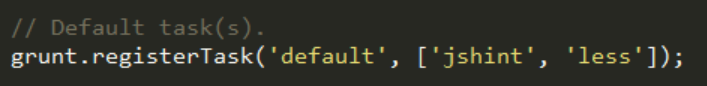
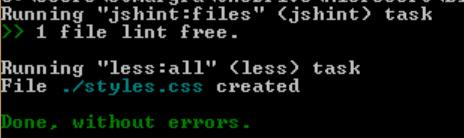
From now, when you run:
gruntIt will run jshint, then less:
You can add any task you want, and you can also specify other group of task like default and call them by passing their name as an argument to the grunt command line.
Easy right?
Step 6. Use watch so you do not have to run grunt manually
Now, you are a happy developer. All you repetitive tasks are automated inside a grunt workflow and you just have to run grunt for them to execute. But that can be done even more easily. That can be done automatically.
To do that, you can add a specific task named watch. This task will constantly inspect your working folder and, based on rules, when a file is modified, grunt will run an associated task.
First, install watch in your project folder:
npm install grunt-contrib-watch –save-dev
Load it like all other tasks using the loadNpmTasks function and configure it. The config part is a bit different here because you need to specify a configuration for each task you want to cover using watch.
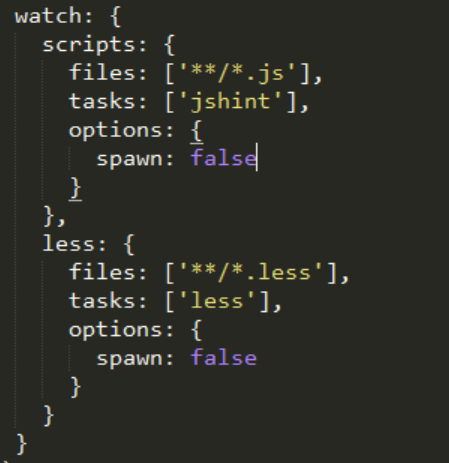
You can find the full documentation for this task here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/grunt-contrib-watch
When you want to activate watch you only have to run the following command:
grunt watch
And it will execute tasks each time a file is changed and this file is in the scope of watched files for the specific task.
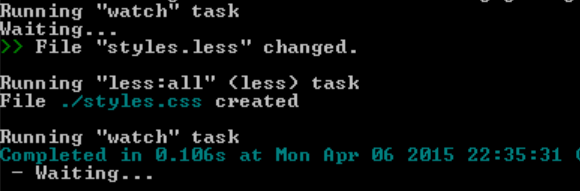
And that’s it! You now know everything to create automated workflow using grunt.
Gulp
What is Gulp?
Gulp is an alternative to grunt. It is a bit more recent and has a reputation as being more flexible than grunt. Before choosing which one you will use, let’s have a look at how gulp works.
Gulp (http://gulpjs.com/) is a workflow automation tool. Like grunt, it works using npm and the package.json file. All available plugins will also be downloaded using npm and added as devDependencies in the package.json file.
One of the main differences with Gulp is that it uses streams. A stream is a set of functions through which a file will go and be modified in memory. The file will be written on the disk only at the end of the process so it is more efficient. Grunt tasks, on the other hand, work as silos and cannot be chained.
Let’s have a quick look at how Gulp works by following a few easy steps.
Step 1. Create the package.json file
Similar to Grunt, you first have to create the package.json file. You can use the exact same technique you used for the grunt sample.
Step 2. Install Gulp and gulp-util globally and locally
Once the package.json file is created, install gulp globally and locally using:
npm install -g gulpand
npm install gulp --save-devThis will install the gulp command line and everything needed to run a gulp workflow.
You then have to install gulp utils which contains common function shared by other plugins:
npm install gulp-util --save-devFinally, create the minimum gulp file which will look like this:
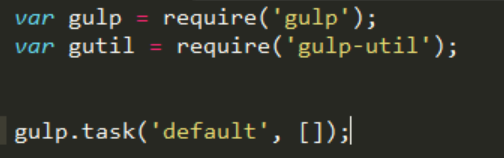
As you can see it is a bit different from the grunt syntax. In gulp, plugins are loaded using the require syntax as you might be used to if you are a nodeJS developer. There is also a default task defined using the gulp.task function.
If you run the gulp command line using a command prompt in the project folder, you should see a result like this:
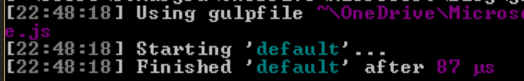
Step 3. Using your first task: Less compilation
To use a plugin in gulp, you use the same function as the one we used to create the default task. This is because you do not have to use a specific name to create a task. You just call gulp.task, set the name you want and give it a JavaScript function as a second parameter. When gulp runs the task, it will run this function.
To use a plugin, you call it using the name you chose when require-ing it. Usually, you call it as part of a streaming workflow which generally starts with a selection of files. This is done with the gulp.src function. It will select a bunch of files and return a stream that can be used by another function using pipe. That is how you can chain multiple actions without writing them to the disk. You just pass the stream from one plugin to another.
Here is a simple sample for less:
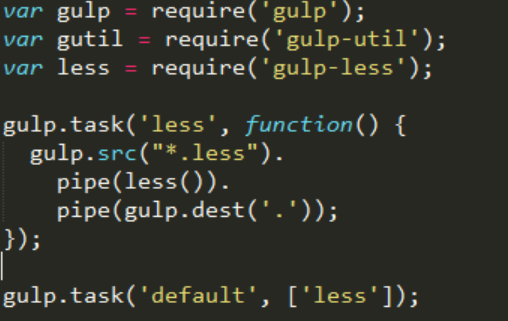
We first require (‘gulp-less’) to load the less plugin for gulp. (We got it using npm install gulp-less --save-dev).
Then gulp.src will select all the .less files, we ‘pipe’ it to the less()function and it finally is ‘piped’ to gulp.dest which indicates where to write the result. As gulp.src can select more than one file, gulp.dest specifies a folder.
Once you understand the piping model, you can easily get the same result as the one we got using grunt.
The power of gulp is that you can create custom task in which you call more than one plugin and where you can associate them the way you want.
Note: there is obviously also a gulp-watch plugin you can use to automated the launch of your workflow!
Conclusion: which one to choose?
I hope that you have now a clearer understanding of why you need an automation workflow and how you can use grunt or gulp to get it.
Choosing one of them is more related to the task you want to achieve.
Grunt is easy to use. You do not have to understand the piping system and achieving simple task will be more straight-forward. It is a really mature tool, used by a lot of known editors and developers and there is a lot of plugins available.
Once that said, the way gulp is designed can give you a lot of flexibility. It has existed for quite some time now and even if you won’t find as many plugins as you will for grunt, all the classic ones are available for gulp.
If you are using a really standard workflow with common steps like jshint, uglifying, css validating etc., Grunt is a good choice. If you are up to more complicated tasks, gulp will be a good wingman.
More information
- Grunt website: http://com/
- Gulp website : http://com
Use grunt inside Microsoft Visual Studio:http://www.asp.net/vnext/overview/aspnet-vnext/grunt-and-bower-in-visual-studio-2015
More hands-on with JavaScript
Microsoft has a bunch of free learning on many open source JavaScript topics and we’re on a mission to create a lot more with Microsoft Edge. Here are some to check-out:
- Microsoft Edge Web Summit 2015 (a complete series of what to expect with the new browser, new web platform features, and guest speakers from the community)
- Build of //BUILD/ and Windows 10 (including the new JavaScript engine for sites and apps)
- Advancing JavaScript without Breaking the Web (Christian Heilmann’s recent keynote)
- Hosted Web Apps and Web Platform Innovations (a deep-dive on topics like manifold.JS)
- Practical Performance Tips to Make your HTML/JavaScript Faster (a 7-part series from responsive design to casual games to performance optimization)
- The Modern Web Platform JumpStart (the fundamentals of HTML, CSS, and JS)
And some free tools to get started: Visual Studio Code, Azure Trial, and cross-browser testing tools – all available for Mac, Linux, or Windows.
This article is part of the web dev tech series from Microsoft. We’re excited to share Microsoft Edge and the new EdgeHTML rendering engine with you. Get free virtual machines or test remotely on your Mac, iOS, Android, or Windows device @ modern.IE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Grunt and Gulp for Workflow Automation
What are the key differences between Grunt and Gulp?
Grunt and Gulp are both JavaScript task runners, but they have some key differences. Grunt focuses on configuration, where you declare tasks and what to do with them. On the other hand, Gulp uses a code-over-configuration approach, where tasks are defined by coding them directly. This makes Gulp more flexible and easier to use for developers who prefer coding over configuration. However, Grunt has a larger plugin ecosystem, which can be beneficial for complex projects.
How can I convert a Grunt script to Gulp?
Converting a Grunt script to Gulp involves understanding the tasks in the Grunt script and then writing equivalent tasks in Gulp. This requires a good understanding of both Grunt and Gulp. You’ll need to identify the plugins used in the Grunt script, find equivalent Gulp plugins, and then write Gulp tasks using these plugins.
What are some common use cases for Grunt and Gulp?
Grunt and Gulp are commonly used for automating repetitive tasks in the development workflow. This includes tasks like minifying JavaScript files, compiling Sass or LESS files into CSS, linting code, running tests, and reloading the browser automatically whenever a file is saved.
How can I get started with Gulp?
To get started with Gulp, you’ll first need to install Node.js and npm on your machine. Then, you can install Gulp globally using npm. Once Gulp is installed, you can create a Gulpfile.js in your project root, where you’ll define your tasks.
What are some best practices for using Grunt and Gulp?
Some best practices for using Grunt and Gulp include keeping your tasks small and focused, using plugins to avoid reinventing the wheel, and making sure your tasks are as efficient as possible. It’s also a good idea to document your tasks, so other developers can understand what they do.
Can I use both Grunt and Gulp in the same project?
While it’s technically possible to use both Grunt and Gulp in the same project, it’s generally not recommended. Using both can lead to confusion and unnecessary complexity. It’s usually better to choose one or the other based on your project’s needs and your personal preference.
How can I debug tasks in Gulp?
Gulp has built-in support for sourcemaps, which can help with debugging. You can also use the gulp-debug plugin to log information about each file that passes through the stream.
What are some alternatives to Grunt and Gulp?
Some alternatives to Grunt and Gulp include npm scripts, webpack, and Parcel. These tools can also automate tasks in your development workflow, and they each have their own strengths and weaknesses.
How can I optimize my Grunt or Gulp tasks?
There are several ways to optimize your Grunt or Gulp tasks. One way is to use the gulp-changed plugin, which only processes files that have changed since the last time the task was run. Another way is to use gulp-parallel to run tasks in parallel, which can speed up your build process.
How can I handle errors in Grunt or Gulp?
Both Grunt and Gulp have ways to handle errors. In Grunt, you can use the –force option to continue running tasks even if one fails. In Gulp, you can use the .on(‘error’) method to handle errors in a stream.
Etienne Margraff is a Technical Evangelist for Microsoft. He’s a core contributor to the Vorlon.js project. Read his blog for follow him on Twitter.


