Integrating with Facebook Graph API
Integrating with Facebook from PHP is easy with the help of Facebook’s PHP SDK and some HTTP libraries like Zend_Http_Client or PEAR HTTP_Request2. In this article I’ll show you how to get started using the Facebook PHP SDK. You’ll learn about the Facebook Graph API and create a Facebook application capable of updating your status message and uploading photos.
If you don’t have it already, you can clone or download the PHP SDK from GitHub. You’ll also need a verified Facebook account.
Key Takeaways
- Facebook’s PHP SDK and HTTP libraries like Zend_Http_Client or PEAR HTTP_Request2 simplify the process of integrating with Facebook from PHP, allowing for the creation of applications that can update statuses and upload photos.
- Registering your application on Facebook is the first step, followed by specifying how your app will integrate with Facebook, such as through a website, a Facebook Canvas page, a mobile site, a native iOS/Android app, or a Facebook page tab.
- The Facebook object defined by the PHP SDK provides the functionality to connect and interact with Facebook, while the Graph API provides an interface to access Facebook’s social graph, allowing for reading and writing of user data.
- The PHP SDK abstracts working with OAuth authentication and the Facebook Graph API, making it easier to create applications that interact with Facebook, however, developers must be aware of certain limitations such as data accessibility and request rate limits.
Registering your App on Facebook
You first need to register your application on Facebook. Go to developers.facebook.com/apps and click the Create New App button at the top of the page.
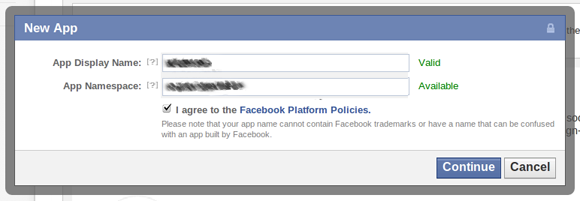
The dialog that opens asks you for the name and a namespace for your application. App Display Name is the name for your application that will be shown to the users. App Namespace is the namespace your application will use for Open Graph and Canvas Page.
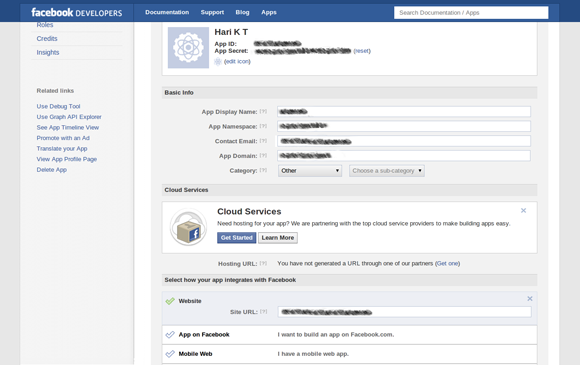
After you register the application, you’ll be taken to the Basic Settings screen on which you need to specify how your app will integrate with Facebook:
- Website – The website option is used for adding social functionality to your website.
- App on Facebook – This Facebook app option embeds your application within a Facebook Canvas page. The code is hosted on your servers, but executes within the context of a Facebook page, similar to an IFrame.
- Mobile Web – The mobile web option is similar to the Website integration option, although it’s intended for mobile sites.
- Native iOS/Android App – The native options allow you to integrate Facebook data in your iOS and Android applications.
- Page Tab – The tab option exposes your application as a Facebook page tab.
For the purposes of this article I’ll use the website integration option. My application will be a stand-alone website, and after authorization Facebook will redirect the user to a specified URL. Select the check mark next to the option and enter the URL for your application’s entry page. Then be sure to click the Save Changes button at the bottom of the page.
You should also make a note of the App ID and App Secret values at the top of the page since you will need these values to connect your application to Facebook.
Using the SDK
Functionality to connect and interact with Facebook is exposed through the Facebook object defined by the PHP SDK. The constructor accepts an array of parameters which contain information about your application, such as the App ID and App Secret that appear on your application’s Basic Settings page.
<?php
session_start();
require_once "php-sdk/src/facebook.php";
$config = array(
"appId" => FACEBOOK_APP_ID,
"secret" => FACEBOOK_APP_SECRET);
$fb = new Facebook($config);Authorization
The getUser() method is used to retrieve the user ID of a Facebook user. The information may or may not be available, depending on whether the user is logged in or not. If the method returns 0 then you know the user has not logged in.
<?php
$user = $fb->getUser();The login link which serves the starting point for the OAuth authentication process with Facebook is obtained using the
getLoginUrl() method. getLoginUrl()
accepts an array of a parameters in which I’ve supplied redirect_uri and scope.<?php
$params = array(
"redirect_uri" => REDIRECT_URI,
"scope" => "email,read_stream,publish_stream,user_photos,user_videos");
echo '<a href="' . $fb->getLoginUrl($params) . '">Login</a>';The redirect_url should be the same address you provided for Site URL when registering the application. The scope is a comma-separated list of requested permissions the application requires. Applications are allowed to access public profile information and other defaults as permitted by Facebook when the user is logged in, but if you want access to additional functionality (such as posting status messages) you must be authorized by the user to do so. The Facebook developers documentation has a list of available permissions. Here I’ve requested permission to to access the user’s email address, read and publishing status updates, post photos, and post videos.
Regardless if the user accepts the request and logs in to Facebook, or rejects the request, he will be redirected back to the redirect_uri and several values will be available as URL parameters. A rejection will include error, error_reason, and error_description parameters:
http://example.com/facebook/myapp.php?error=access_denied&error_reason=user_denied&error_description=The+user+denied+your+request.
A successful authentication/authorization will append a code parameter, like so:
http://example.com/facebook/myapp.php?code=TOKEN_VALUE
The code is then used to request an Access Token:
https://graph.facebook.com/oauth/access_token?client_id=FACEBOOK_APP_ID&redirect_uri=FACEBOOK_REDIRECT_URI&client_secret=FACEBOOK_APP_SECRET&code=TOKEN_VALUE
As you’re using the SDK which handles all of this for you, I won’t go more into how OAuth works. If you’re interested in learning more read Dustin Runnell’s Understanding OAuth article and the SDK’s documentation on authentication. (Facebook uses OAuth v2 and Dustin’s article covers v1, but it will still give you a good idea of the role requests and credentials play in the process).
The Graph API
Once the user grants permission, you can read the user’s feed of status messages with a GET request:
https://graph.facebook.com/me/feed?access_token=ACESS_TOKEN
Alternatively, you can use the api() method which wraps a call to Facebook Graph API methods:
<?php
$data = $fb->api("/me/feed");The
api()
method in this case can accept three arguments: the Graph API path for the request, the HTTP method for the request (defaults to GET), an an array of parameters specific to the Graph API method.
The Graph API provides an interface to access the members and relationships in Facebook’s social graph. Each member has a unique ID and can be accessed in a REST-like manner through resources starting with “https://graph.facebook.com”. For example, sending a GET request with your browser for:
https://graph.facebook.com/harikt
will return a JSON object with basic public information about me and my profile.
{
"id": "596223095",
"name": "Hari Kt",
"first_name": "Hari",
"last_name": "Kt",
"link": "http://www.facebook.com/harikt",
"username": "harikt",
"gender": "male",
"locale": "en_US"
}
Some requests require an Access Token. Requesting a feed of message updates is a privileged action, and so sending a GET request for:
https://graph.facebook.com/harikt/feed
will return a JSON object populated with information about an OAuthException error.
{
"error": {
"message": "An access token is required to request this resource.",
"type": "OAuthException"
}
}
The ID me is a convenient shorthand which refers to the current user.
To add an update to the user’s feed using the api() method, you would make a POST request to /me/feed and supply a message value.
<?php
$data = array("message" => "Hello World!");
$status = $fb->api("/me/feed", "POST", $data);To upload a new photo you would make a
POST request to /me/photos (or ALBUM_ID/photos to upload to a specific album) and supply an array with name and image arguments.<?php
$fb->setFileUploadSupport(true);
$data = array(
"name" => "a vacation photo",
"image" => "@/home/hari/vacation/img42.jpg");
$status = $fb->api("/me/photos", "POST", $data);The SDK uses PHP’s cURL extension to post data, and calling
setFileUploadSupport() with true will provide the data values to CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS as an array which in turn causes cURL to encode the data as “multipart/form-data”. Also cURL-related is the use of @ before the full path of the image to be posted. See the description for CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS in PHP’s documentation of curl_setopt() for more information.
To learn more about Facebook’s Graph API I recommend you to read the Graph API documentation and experiment with the Graph API Explorer which is quite a handy utility.
Your First Application
Let’s bring together everything you’ve learned now and write a very basic example of a Facebook application. It will prompt the user to log in and authorize the application, and then enable him to update his status message and upload a photo.
<?php
session_start();
require_once "php-sdk/src/facebook.php";
$config = array(
"appId" => FACEBOOK_APP_ID,
"secret" => FACEBOOK_APP_SECRET);
$fb = new Facebook($config);
$user = $fb->getUser();
?>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello Facebook</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
if (!$user) {
$params = array(
"scope" => "read_stream,publish_stream,user_photos",
"redirect_uri" => REDIRECT_URI);
echo '<a href="' . $fb->getLoginUrl($params) . '">Login</a>';
}
else {
?>
<form action="<?php echo $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"];?>" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<textarea name="message" id="message" rows="2" cols="40"></textarea><br>
<input type="file" name="image" id="image"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Update">
</form>
<?php
// process form submission
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST" && !empty($_POST["message"])) {
if (is_uploaded_file($_FILES["image"]["tmp_name"])) {
$finfo = finfo_open(FILEINFO_MIME_TYPE);
$mime = finfo_file($finfo, $_FILES["image"]["tmp_name"]);
$allowed = array("image/gif", "image/jpg", "image/jpeg", "image/png");
// upload image
if (in_array($mime, $allowed)) {
$data = array(
"name" => $_POST["message"],
"image" => "@" . realpath($_FILES["image"]["tmp_name"]));
$fb->setFileUploadSupport(true);
$status = $fb->api("/me/photos", "POST", $data);
}
}
else {
// update status message
$data = array("message" => $_POST["message"]);
$status = $fb->api("/me/feed", "POST", $data);
}
}
if (isset($status)) {
echo "<pre>" . print_r($status, true) . "</pre>";
}
}
?>
</body>
</html>The code presents a link to log in or out as appropriate depending on the return value of
getUser(). Then, a simple HTML form is displayed which permits the user to enter a status message and possibly an image file. When the user submits the form, the code verifies the uploaded image if one is provided and posts it to Facebook, or performs just a status message update.
Summary
The code here is for demonstration purposes, and I’ve omitted a lot of filtering and security-related checks you’d want to perform when writing a real-world application. It does however highlight the main points presented in this article. The Facebook PHP SDK makes integrating with Facebook easy. It abstracts working with OAuth authentication and the Facebook Graph API.
Image via mkabakov / Shutterstock
Frequently Asked Questions about Integrating with Facebook
What is Facebook API and why is it important?
Facebook API, also known as Facebook Graph API, is a tool that allows developers to read from and write data into Facebook. It provides the ability to create, read, update, and delete data on Facebook, which includes posts, comments, likes, photos, and other user data. This is important because it allows developers to create applications that can interact with Facebook, providing a more integrated and personalized user experience.
How can I get started with Facebook API?
To get started with Facebook API, you first need to create a Facebook Developer account. Once you have an account, you can create a new app, which will provide you with an App ID and App Secret. These are used to authenticate your app with Facebook. You can then use the Graph API Explorer to start making requests to the API.
What are the different types of Facebook APIs?
Facebook provides several different APIs, each designed for a specific purpose. The Graph API is the primary way to get data in and out of Facebook’s platform. The Marketing API allows businesses to automate and scale their Facebook advertising. The Pages API allows apps to access and update a Facebook Page’s posts and comments. The Instagram Graph API allows apps to access and interact with data on Instagram.
How can I use Facebook API to integrate with my website?
You can use Facebook API to integrate various features into your website. For example, you can use the Login API to allow users to log into your website using their Facebook credentials. You can also use the Graph API to display a user’s Facebook posts on your website, or the Comments API to allow users to comment on your website using their Facebook account.
What are the limitations of Facebook API?
While Facebook API provides a lot of functionality, there are some limitations. For example, not all data is accessible through the API. Some data, such as private user data, is protected and cannot be accessed without the user’s explicit permission. Additionally, there are rate limits on how many requests an app can make to the API in a given time period.
How can I handle errors in Facebook API?
Facebook API returns error codes and messages when a request fails. You can use these error codes to determine what went wrong and how to fix it. For example, if you receive an error code indicating that you have exceeded the rate limit, you can implement a retry strategy to wait and then retry the request.
How can I ensure the security of my app when using Facebook API?
There are several best practices you can follow to ensure the security of your app when using Facebook API. Always use HTTPS when making requests to the API. Store your App ID and App Secret securely and never include them in client-side code. Also, regularly review the permissions your app is requesting to ensure it is only requesting the data it needs.
Can I use Facebook API to post content on behalf of users?
Yes, you can use the Publishing API to post content on behalf of users. However, this requires the ‘publish_actions’ permission, which must be granted by the user. Additionally, all content posted on behalf of users must comply with Facebook’s Community Standards and Platform Policy.
How can I test my app’s integration with Facebook API?
Facebook provides a tool called the Graph API Explorer, which allows you to make requests to the API and see the responses in real-time. This can be a useful tool for testing your app’s integration with the API.
What resources are available to help me learn more about Facebook API?
Facebook provides extensive documentation on their developer website, including guides, tutorials, and reference material for each of the APIs. There are also many online communities and forums where developers share tips and tricks, ask questions, and help each other troubleshoot issues.
Hari K T is a Freelance LAMP developer/consultant, open-source contributor auraphp and speaker.
