
Cloud computing has completely changed how individuals and businesses interact with technology. It helps users run complex workflows on the cloud without worrying about capacity, security concerns or management.
For instance, if you’ve tried to self-host an application, you would’ve done the following:
- Built an on-premise server.
- Managed the server room by providing comprehensive cooling.
- Monitored the server resources and upgraded the server capacity, such as the RAM and CPU, as the workload increased.
This required lots of effort, sometimes more difficult than building the application. In most cases, managing your own server is expensive, as you have to buy the server with enough RAM, and you always have a limitation on vertically scaling a server. So, there’s a high chance you’d either over-provision or under-provision your server.
However, the introduction of the cloud is simpler, as the cloud vendor provides you with the resources to use on an on-demand basis. You have to focus on building and deploying your application while the cloud vendor takes care of your infrastructure.
So, let’s look at what is cloud computing with examples and the benefits it offers to individuals and organizations.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud computing delivers IT services over the internet, including storage, servers, databases, and software.
- It provides scalability, cost efficiency, and accessibility, making it a preferred choice for businesses and individuals.
- Key players include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, each offering unique services and benefits.
- Emerging trends like edge computing and AI integration are shaping the future of cloud technology.
Understanding Cloud Computing
What Is Cloud Computing Services?
If you’re looking for what is cloud computing in simple terms, think of it as renting computing power and storage online instead of buying physical servers.
If we go a bit deeper, cloud computing refers to delivering computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“cloud”). This eliminates the need for businesses and individuals to maintain physical IT infrastructure, enabling access to resources on demand without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
If you’re going ahead with the cloud deployment, you should understand that it has a set of key features that make it extremely powerful:
Scalability
Easily scale resources up or down based on needs. This means that you don’t need to over-provision or under-provision your resources, but rather let the cloud decide when to scale your resource up and down based on the workload.
Cost-Efficiency
Pay only for what you use, reducing capital expenditure. You don’t need to provision your resources thinking you’re going to be serving 1000 users. You can start small, and grow when needed.
Accessibility
Access resources from anywhere with an internet connection. This means you can work seamlessly across different devices—whether it’s a laptop, tablet, or smartphone.
Automation
Many processes, like updates and maintenance, are automated. Cloud vendors offer managed services like Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda that handle features like patch management automatically. You don’t need to worry about securing the underlying infrastructure as that’s taken care of by the vendor.
However, you need to be mindful about the overall application security. This is clearly defined in the Shared Responsibility Model of the cloud. While AWS takes care of securing the underlying infrastructure, you need to secure your application.
Now, let’s see what are the different types of cloud systems.
Types of Cloud Computing
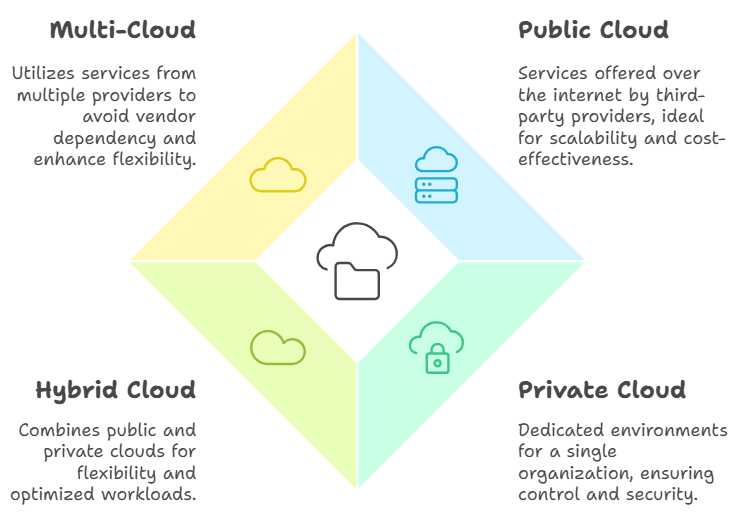
There are 4 main types of the cloud computing architecture models that you can select:
1. Public Cloud
Services are offered over the public internet by third-party providers like AWS and Google Cloud. Public clouds are ideal for businesses that need scalability and cost-effectiveness. They provide a shared environment where resources are managed by the provider, making them highly accessible and easy to deploy.
2. Private Cloud
These are cloud environments that are dedicated to a single organization. Private clouds are tailored for businesses requiring greater control and security. They are often hosted on-premises or at a data center managed by a third-party provider, ensuring data isolation and compliance with specific regulatory needs.
3. Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, offering flexibility and optimized workloads. A hybrid cloud setup allows organizations to run sensitive workloads in a private environment while leveraging the public cloud for less critical tasks. This ensures cost efficiency while maintaining data security where needed.
4. Multi-Cloud
Utilizes services from multiple cloud providers to avoid dependency on a single vendor. Multi-cloud strategies provide redundancy, enhanced performance, and greater flexibility. Businesses can select the best services from each provider, tailoring their infrastructure to meet specific requirements without being locked into a single ecosystem.
Comparing Major Cloud Providers
Several cloud service providers have been highlighted under Gartner’s Magic Quadrant. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud visionary and has been one for the past 10 years. However, there are several other cloud vendors that are widely recognized, such as GCP, Oracle and Azure.
However, AWS stands on top of the rest due to its constant innovation in the cloud and its massive number of cloud service models and offerings.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a market leader in cloud computing, offering a broad range of services and a mature ecosystem. Its global presence ensures high availability and scalability, making it an excellent choice for startups and large enterprises. AWS provides advanced tools for machine learning, data analytics, and IoT, catering to diverse business needs. Companies seeking flexibility and cutting-edge capabilities often choose AWS for its robust performance and extensive service catalog.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure excels in seamless integration with Microsoft’s existing products, such as Windows Server, SQL Server, and Office 365. Its enterprise-grade support makes it a preferred choice for organizations already entrenched in the Microsoft ecosystem. Azure’s hybrid cloud capabilities and focus on security and compliance make it ideal for industries like healthcare and finance. Businesses leveraging Microsoft tools can benefit significantly from Azure’s streamlined operations and cost-effective solutions.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) stands out for its strength in AI and machine learning. GCP’s TensorFlow and BigQuery are popular tools for data scientists and developers aiming to build advanced analytics solutions. Its cost-effective pricing structure and focus on sustainability appeal to businesses managing large-scale data applications. GCP is an excellent choice for data-intensive industries such as technology, education, and research.
Other Providers
- IBM Cloud specializes in enterprise-grade security and AI capabilities. It is often chosen by businesses in need of robust data protection and advanced AI services, particularly in regulated industries like healthcare and banking.
- Oracle Cloud is renowned for its strong database management services. Its cloud infrastructure is well-suited for enterprises relying on Oracle databases and enterprise applications. Oracle’s focus on performance and reliability makes it a top choice for critical business workloads.
Managing Cloud Costs
So, if you’re looking to adopt any of these cloud vendors and start utilizing their cloud infrastructure services now, it’s important that you look at cost. No matter how good the cloud is, there are always ways you can go wrong and end up with a massively large cloud bill.
So, here are some strategies to optimize cloud costs effectively:
Right-Sizing Resources
Many organizations over-provision cloud storage and computing resources, leading to unnecessary expenses. Right-sizing involves analyzing workloads and adjusting resources to match actual usage. This ensures that you pay only for what you need, reducing waste.
Usage Monitoring
Regularly monitor your cloud computing costs and usage with tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure’s Cost Management and Billing. These tools provide insights into spending patterns, helping identify areas where costs can be reduced. For example, spotting underutilized virtual machines can lead to immediate savings.
Reserved Instances
Cloud service providers offer significant discounts for committing to long-term usage through reserved instances. By forecasting future needs and opting for these plans, businesses can achieve cost reductions of up to 75% compared to on-demand pricing.
Avoiding Overlooked Costs
Hidden expenses, such as data transfer fees or idle resources, can inflate cloud bills. Implement automated alerts to detect unused storage or running instances. Additionally, establish policies for managing your data storage and transfers and archiving old data to control these costs effectively.
Regular Audits and Reviews
Conduct periodic cost audits to ensure alignment with business goals. These audits can uncover new opportunities for optimization, such as transitioning workloads to more cost-efficient regions or leveraging alternative pricing models.
By adopting these strategies, you can maximize your cloud investments while minimizing unnecessary expenditures.
Concluding Thoughts
And that’s pretty much on cloud computing.
In a nutshell, cloud computing is more than a technology; it’s a transformative approach to leveraging IT resources. From cost-efficiency to scalability and innovation, the cloud has become indispensable for modern businesses. By understanding what is cloud computing definition, leveraging best practices, and staying updated on emerging trends, organizations can harness cloud computing benefits to their full potential to drive growth and innovation.
FAQs on Cloud Computing
What Is Cloud Technology in Simple Terms?
Cloud computing software is a way to access IT resources like storage and applications, as well as remote servers over the internet, without owning physical hardware.
What Are Cloud Solutions?
Cloud solutions refer to services provided through the cloud, such as SaaS (Software as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
What Is a Cloud Environment?
A cloud environment is a setup where cloud resources operate, including both private and public clouds, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud models.
What Is Cloud Software?
Cloud software refers to applications and programs that are hosted on cloud servers and accessed over the internet. Unlike traditional software that requires installation on local devices, cloud software operates entirely online, allowing users to access it from any device with an internet connection.
What Is Cloud Programming?
Cloud programming involves writing software specifically designed to run on cloud platforms. Developers use tools and languages like Python, Java, or Go to create scalable and efficient applications that leverage the cloud’s distributed architecture.
What Is Meant by Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
Key benefits include flexibility, cost savings, enhanced collaboration, and access to advanced tools like AI and analytics.
With this understanding, businesses and individuals can explore the world of using cloud computing services, ensuring they remain competitive and innovative in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
How Secure Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing offers robust security measures such as encryption, firewalls, and access controls. However, security responsibilities are shared between the provider and the user. While the provider secures the infrastructure, the user must secure their applications, data, and access.
What Are the Different Cloud Service Models?
The three primary cloud service models are:
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Access software over the internet without installation. Examples: Gmail, Dropbox.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Use cloud platforms to develop and deploy applications. Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Rent virtualized computing resources like servers and storage. Examples: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine.
Can Cloud Computing Be Used Offline?
Generally, cloud computing requires an internet connection. However, some services provide offline access features that synchronize data once the connection is restored.
What Is Serverless Computing?
Serverless computing allows you to run applications and services without managing underlying servers. The cloud provider automatically provisions resources as needed. Examples include AWS Lambda and Azure Functions.
Dianne is SitePoint's newsletter editor. She especiallly loves learning about JavaScript, CSS and frontend technologies.




