This tutorial will show you how to collect and validate HTML form data using the two-way data binding of AnguarlJS. In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to implement a simple user registration form using Angular. Along the way, we’ll look at basic HTML and show what needs to be changed in order to incorporate AngularJS.
Prerequisities
- Install Node.js.
- Clone the AngularJS seed project.
Form HTML
The HTML for our signup form is shown below. Bootstrap has been used to make the site more visually appealing.<html lang="en" ng-app="myApp">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Bootstrap 101 Template</title>
<link href="css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/app.css" />
</head>
<body>
<form class="form-horizontal" role="form">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputName3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Name</label>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input class="form-control" id="inputName3" placeholder="Name">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input class="form-control" id="inputEmail3" placeholder="Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">Sign up</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
<script src="lib/common/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="lib/common/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script src="lib/angular/angular.js"></script>
<script src="lib/angular/angular-route.js"></script>
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
<script src="js/services.js"></script>
<script src="js/controllers.js"></script>
<script src="js/filters.js"></script>
<script src="js/directives.js"></script>
</body>
</html>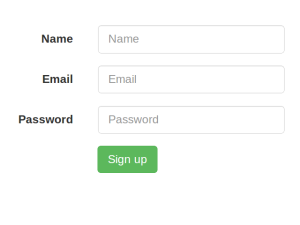
Collecting Data
In jQuery, individual form inputs are read using code like this:$('#txtInput').val()$scope. To verify this, add the following span to the HTML before the closing form tag. This snipper relies on a variable named formInfo.
<span>{{formInfo}}</span>ng-model which helps to bind an input to a variable. Let’s apply the ng-model directive to the three input elements in the form. Here is the updated HTML form:
<form class="form-horizontal" role="form">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputName3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Name</label>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input class="form-control" id="inputName3" placeholder="Name" ng-model="formInfo.Name">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input class="form-control" id="inputEmail3" placeholder="Email" ng-model="formInfo.Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-4">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="Password" ng-model="formInfo.Password">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">Sign up</button>
</div>
</div>
<span>{{formInfo}}</span>
</form>ng-model directive has been attached to each of the input elements. Each input is bound to a specific field in the formInfo object. Now, as the user enters data into the input elements, formInfo automatically gets updated. You can see this code in action by looking at this working demo. Using the same formInfo variable we can access the form data without reading each element value individually inside our controller. For that, we need to define a $scope.formInfo variable inside our controller, MyCtrl1. After making these changes, this is what app/js/controllers.js looks like:
'use strict';
/* Controllers */
angular.module('myApp.controllers', []).
.controller('MyCtrl1', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.formInfo = {};
$scope.saveData = function() {
};
}])
.controller('MyCtrl2', [function() {
}]);saveData() which will be called when the user clicks the Sign Up button.
Next, we need to attach a ng-controller directive to the form itself.
<form class="form-horizontal" role="form" ng-controller="MyCtrl1">ng-click directive to the Sign Up button:
<button type="submit" ng-click="saveData()" class="btn btn-success">Sign up</button>saveData() function, add a console.log($scope.formInfo); just to check if we are getting the form data collection in our controller using the $scope. Restart the node server, browse to the HTML page, and check your browser console. You should see some thing like this:
Object {Name: "Jay", Email: "jay3dec@gmail.com", Password: "helloworld"}Validating the Inputs
We also need to validate, if the data that we received from the$scope is valid. If it’s not, we must show some validation errors. The ng-show directive shows or hides an element based on the value of an expression. We’ll be using it to show error messages. Begin by defining three $scope variables – $scope.nameRequired, $scope.emailRequired, and $scope.passwordRequired. We’ll validate the name, email, and password in the saveData() function as shown in the updated app/js/controllers.js.
'use strict';
/* Controllers */
angular.module('myApp.controllers', [])
.controller('MyCtrl1', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.formInfo = {};
$scope.saveData = function() {
$scope.nameRequired = '';
$scope.emailRequired = '';
$scope.passwordRequired = '';
if (!$scope.formInfo.Name) {
$scope.nameRequired = 'Name Required';
}
if (!$scope.formInfo.Email) {
$scope.emailRequired = 'Email Required';
}
if (!$scope.formInfo.Password) {
$scope.passwordRequired = 'Password Required';
}
};
}])
.controller('MyCtrl2', [function() {
}]);span for each input element to display error message as shown below;
<span ng-show="nameRequired">{{nameRequired}}</span>
<span ng-show="emailRequired">{{emailRequired}}</span>
<span ng-show="passwordRequired">{{passwordRequired}}</span>Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to read data from a form and validate it using AngularJS. I would recommend reading the AngularJS API docs for deeper insight. In the meantime, a working demo is available here.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about HTML Forms in AngularJS
What is AngularJS and why is it used in HTML forms?
AngularJS is a powerful JavaScript framework developed by Google. It is used to build dynamic, single-page applications (SPAs). When used in HTML forms, AngularJS provides a way to handle user inputs and validations effectively. It allows you to create more interactive and responsive forms, enhancing the overall user experience.
How do I start using AngularJS in my HTML forms?
To start using AngularJS in your HTML forms, you first need to include the AngularJS library in your HTML file. You can do this by adding a script tag with the AngularJS CDN link. Once the library is included, you can use the ‘ng-app’ directive to define the AngularJS application and ‘ng-controller’ directive to control the application data.
What are directives in AngularJS and how are they used in HTML forms?
Directives are markers on a DOM element (such as an attribute, element name, comment or CSS class) that tell AngularJS’s HTML compiler to attach a specified behavior to that DOM element. In HTML forms, directives like ‘ng-model’, ‘ng-bind’, ‘ng-app’, ‘ng-controller’, etc., are used to bind input fields to variables, control the scope of the data, and handle form validations.
How does data binding work in AngularJS HTML forms?
Data binding in AngularJS is the automatic synchronization of data between the model and view components. The ‘ng-model’ directive is used to bind input fields to variables in the controller. This means that any change in the input field will automatically update the variable value and vice versa.
How can I validate user input in AngularJS HTML forms?
AngularJS provides several built-in directives for form validation, such as ‘required’, ‘ng-minlength’, ‘ng-maxlength’, ‘ng-pattern’, etc. These directives can be used in the input fields to validate the user input based on certain conditions. If the input does not meet the conditions, the form will not be submitted.
How can I display error messages in AngularJS HTML forms?
You can display error messages in AngularJS HTML forms using the ‘ng-show’ or ‘ng-hide’ directives. These directives can be used to show or hide error messages based on the validity of the form or input fields.
How can I submit an AngularJS HTML form?
You can submit an AngularJS HTML form using the ‘ng-submit’ directive. This directive binds the form submission to a function in the controller which gets executed when the form is submitted.
How can I reset an AngularJS HTML form?
You can reset an AngularJS HTML form using the ‘type=reset’ button. This will reset all the form fields to their initial values.
Can I use AngularJS with other JavaScript libraries in my HTML forms?
Yes, AngularJS can be used with other JavaScript libraries in your HTML forms. However, you need to ensure that there are no conflicts between the libraries.
How can I handle complex form validations in AngularJS?
For complex form validations, you can write custom directives in AngularJS. These directives can contain the validation logic and can be used in the form fields.
 Jay Raj
Jay RajJay is a Software Engineer and Writer. He blogs occasionally at Code Handbook and Tech Illumination.