Because this site has a truly global audience, you the reader could be anywhere in the world. Were I to ask you where on Earth you are, you might volunteer the name of a city, a state, or perhaps just the country you’re in. The answer might be ambiguous – is that Paris, France or Paris, Texas? Modern geolocation applications use latitude and longitude to identify the location of people and of places to within a few meters, but it’s highly unlikely you’ll answered the question with those. Geolocation – that is, obtaining your location using GPS, Wi-Fi triangulation, or perhaps using your IP address – is all very well and good, but sometimes you just need to ask someone where they are. The challenge then is to do two things: work out what place you could be talking about, disambiguate if necessary, and then identify exactly where on Earth that is. That’s what I’ll show you how to do in this article; by using a freely available web service, we’ll write a simple program to ask users where they are (and ask them to clarify if necessary) before identifying their responses in concrete terms.
Where On Earth Identifiers (WOEIDs)
I used the phrase “where on Earth” very deliberately as there is a database where places are identified not by name, but by what are called Where on Earth Identifiers (WOEIDs). The WOEID database has been put together and made freely available by Yahoo!, and is also used by Flickr, and for geographic-based trends by Twitter. With every entry is a latitude and longitude for that place, as well as the names people have given them. To complicate this somewhat, there’s not always a one-to-one relationship. What I call Brussels you may call Bruselas, while residents would be more likely to call it Bruxelles. Then there are special cases, such as Peking/Beijing.Getting Started with Placemaker
Yahoo!’s Placemaker web service is a “geo-extraction” service which uses the WOEID database and performs the sort of interpretation we need; parsing free-form text, identifying possible places, and returning information about them, such as the WOEID and that all-important latitude and longitude. Before you can use the Placemaker service, you’ll need an application ID, and in order to do that you’ll need a Yahoo! Id. If you use any of their services, you’ll already have one. Go to the Yahoo! website to generate an application ID where you’ll be asked to fill out the following form:
Making the Request
Placemaker is a REST-like web service with a single endpoint; to use the service you issue a POST request to the URLhttp://wherein.yahooapis.com/v1/document. There are a number of available response types: as well as the standard XML and JSON (and JSONP), you also have the option of obtaining the results in RSS format. Although I normally prefer JSON (a purely personal preference), in this example I’ll use XML.
Let’s look at the five request parameters you’re going to use.
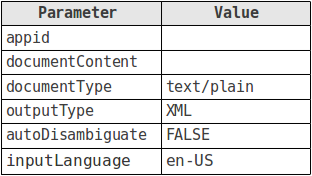
appid, is the application ID you obtained earlier. If you leave this out the request will be rejected. The second, documentContent, will be the string you’re searching for – the parameter named such because the service allows the parsing of entire documents, however I’m really just going to pass the name of a place provided by the user.
The documentType and outputType both refer to the response you’re expecting, though they could be a little confusing; the documentType (of the response) is plain text, while the corresponding outputType is XML. (The documentType would also be plain text if outputType were set to JSON.)
Setting autoDisambiguate false overrides the default behavior of the service, which is to only return the most likely place. It’s this ambiguity we’re looking to resolve ourselves by asking the user rather than letting the service decide for us.
Finally inputLanguage tells the service which language the document (that is to say, the user input) is in; this helps the service to know how to interpret place names. It’s not a required parameter (and predictably it defaults to US English), but it’s worth mentioning because it’s important to remember that a single WOEID can correspond to a number of names in a multitude of languages.
The Code
Now let’s dig into the code then as we start by obtaining the text from the user via POST and make the request.<?php
$appId = YOUR_APP_ID_HERE;
$name = $_POST["name"];
$handle = curl_init("http://wherein.yahooapis.com/v1/document");
curl_setopt($handle, CURLOPT_POST, 1);
curl_setopt($handle, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, sprintf("documentContent=%s&documentType=%s&outputType=%s&autoDisambiguate=%s&appid=%s&inputLanguage=%s",
urlencode($name),
"text/plain",
"xml",
"false",
$appId,
"en-US"));
curl_setopt($handle, CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, 1);
curl_setopt($handle, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($handle);
curl_close($handle);http://wherein.yahooapis.com/v1/document, the POST variables to those discussed earlier, and return the web service’s response as a string. Don’t forget to URL encode the name before passing it via POST though.
Before we start manipulating the response, let’s take a look at what we’re expecting (you might want to echo it out to the screen at this point). Here’s a simplified example of an XML response:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<contentlocation />
<processingTime>0.009052</processingTime>
<version> build 110725</version>
<documentLength>6</documentLength>
<document>
<administrativeScope>..</administrativeScope>
<geographicScope>..</geographicScope>
<localscopes>..</localscopes>
<extents>..</extents>
<placeDetail>..</placeDetail>
<placeDetail>..</placeDetail>
<placeDetail>..</placeDetail>
<placeDetail>..</placeDetail>
...
</document>
</xml>administrativeScope, geographicScope, localscopes, and extents elements.
If you queried “Paris” for example, then it would give you geographic information about the region of Île-de-France, and the country France – but these scopes do not relate to Paris, Texas, or indeed anywhere else that shares that name. It’s those places we’re interested in because we want the user to clarify. These alternatives can be found in the placeDetails elements, as shown below:
<placeDetails>
<placeId>3</placeId>
<place>
<woeId>615702</woeId>
<type>Town</type>
<name><![CDATA[Paris, Ile-de-France, FR]]></name>
<centroid>
<latitude>48.8569</latitude>
<longitude>2.34121</longitude>
</centroid>
</place>
<placeReferenceIds>1</placeReferenceIds>
<matchType>0</matchType>
<weight>1</weight>
<confidence>6</confidence>
</placeDetails>placeDetails element. The placeId represents a given place within the context of the response, and can be used to disambiguate between multiple matches with the same WOEID, although that – along with the placeReferenceIds – is a little beyond the scope of this article.
The weight and confidence tell us more about the match. The weight refers to the relative weight of the place in the document as a whole. This is largely irrelevant in the context of our use of the service, as we’re only sending a fragment of text referring to a single place (at least that’s what we’re asking the user for). Rather, the is used to rank places when a number are mentioned, determined by such factors as their position in the document and the number of mentions. The confidence value (on a scale of 1-10 with 10 being the most certain) is the confidence that this place is actually referred to in the document – but also how confident it is that the place is referred to rather than another place. This last clause is important, because it takes into account the relative likelihood that if 100 people said “London”, the chances are that the majority would mean the capital of England, rather than one of the various, smaller Londons in the United States. In other words, we can sort the results in descending order, based on the value of the confidence.
Finally, and most importantly, there’s the actual place. The place element has a type; this will usually be Town, but may also be State, Suburb or of course Country. The centroid element contains the latitude and longitude of the geometric center, name should be self explanatory, and woeId is the identifier I’ve been talking about. Because this is a widely accepted identifier, there’s nothing to stop us using this to obtain information about the place elsewhere.
Interpreting the Response
Now that we’re familiar with the structure of the response, let’s try and use it. Here’s the code which parses the response:<?php
$places = array();
$xml = simplexml_load_string($response);
foreach ($xml->document->placeDetails as $xmlPlaceDetail) {
$xmlPlace = $xmlPlaceDetail->place;
$xmlCentroid = $xmlPlace->centroid;
$place = new stdClass();
$place->id = (int)$xmlPlaceDetail->placeId;
$place->woeid = (int)$xmlPlace->woeId;
$place->name = (string)$xmlPlace->name;
$place->lat = (float)$xmlCentroid->latitude;
$place->lng = (float)$xmlCentroid->longitude;
$place->confidence = (int)$xmlPlaceDetail->confidence;
$places[$place->id] = $place;
}placeDetail elements. Each time it encounters one, it takes the place and centroid elements to extract the information we’re after, all of which is assigned to a new object representing the place in question.
We now have a list of possibilities; however the service also gives us that measure of how likely it thinks it is that the user will mean one place over another, so let’s sort that array using a simple callback:
<?php
function confidenceSort($a, $b) {
if ($a->confidence == $b->confidence) {
return 0;
}
return ($a->confidence > $b->confidence) ? -1 : 1;
}
uasort($places, "confidenceSort");What Next?
I’ve shown you how to ask the user for a place name, retrieved information about possible options and sorted them according to how likely they mean one location over the other, and a simple demo is available which you can find on GitHub. What you do with this now is up to you – you could ask the user for clarification, or try to reduce the number of alternatives using biasing. Some queries can produce dozens of results, so it’s probably worth trying to influence the search by biasing it towards a given location based on what you know about the user – you can pass the WOEID of a place using thefocusWoeId parameter for just that.
You may wish to read more about WOEIDs, or dig a little deeper by looking at Yahoo!’s Geoplanet service – not just for towns and cities, but landmarks as well. You may also wish to process whole documents – imagine for a moment the possibilities for geotagging blog content, or enhancing a text-based search to find documents not based on text content, but on the location of the user. Have a look through the documentation, play around, and if you get stuck there’s a Placemaker forum on Yahoo! where you can find further information and ask for help.
If you do build anything interesting using this, I’d love to hear about it in the comments!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about WOEID
What is a WOEID and why is it important?
A WOEID, or Where On Earth Identifier, is a unique identifier assigned by Yahoo to refer to any location on Earth. It’s a system that allows for precise identification of any geographical location, from a country down to a town or even a landmark. This is particularly useful in applications that require location-specific data, such as weather forecasting, local news updates, or mapping services. By using a WOEID, these applications can provide accurate and relevant information tailored to a specific location.
How can I find the WOEID of a specific location?
There are several ways to find the WOEID of a specific location. One of the most straightforward methods is to use a WOEID lookup service, such as the one provided by Yahoo’s GeoPlanet. Simply enter the name of the location you’re interested in, and the service will return its WOEID. Alternatively, you can use a mapping service that supports WOEID, such as Yahoo Maps or Bing Maps. By clicking on a location on the map, you can view its WOEID.
Can I use WOEID for my own applications?
Yes, you can use WOEID for your own applications. Yahoo provides a public API that allows developers to access WOEID data. This can be used to incorporate location-specific features into your own applications. However, please note that usage of the API is subject to Yahoo’s terms of service, and you may need to obtain a developer key.
What is the format of a WOEID?
A WOEID is a numeric string that can be up to 11 digits long. It does not contain any letters or special characters. Each WOEID is unique and does not change over time, so once you know the WOEID of a location, you can use it to consistently refer to that location in the future.
How accurate is WOEID?
WOEID is designed to be highly accurate, as it is based on a comprehensive database of geographical locations. However, like any system, it is not infallible. There may be occasional discrepancies or errors, particularly for very small or obscure locations. If you encounter an error, you can report it to Yahoo for correction.
Can I use WOEID to find the latitude and longitude of a location?
Yes, you can use WOEID to find the latitude and longitude of a location. By entering a WOEID into a lookup service or mapping application, you can view the geographical coordinates of the corresponding location. This can be useful for applications that require precise location data.
Is WOEID used worldwide?
Yes, WOEID is used worldwide. It covers all countries and territories, as well as many cities, towns, and landmarks. This makes it a versatile tool for any application that requires location-specific data.
Is WOEID free to use?
Yes, WOEID is free to use. Yahoo provides access to WOEID data through its public API, which is free of charge. However, usage of the API is subject to Yahoo’s terms of service.
Can I use WOEID without an internet connection?
No, you cannot use WOEID without an internet connection. WOEID data is stored on Yahoo’s servers, so you need an internet connection to access it. However, once you have obtained a WOEID, you can store it locally for offline use.
What is the future of WOEID?
The future of WOEID is uncertain, as Yahoo has discontinued many of its services in recent years. However, as of now, WOEID remains available and continues to be used in many applications. It remains a valuable tool for developers and users alike.
Lukas is a freelance web and mobile developer based in Manchester in the North of England. He's been developing in PHP since moving away from those early days in web development of using all manner of tools such as Java Server Pages, classic ASP and XML data islands, along with JavaScript - back when it really was JavaScript and Netscape ruled the roost. When he's not developing websites and mobile applications and complaining that this was all fields, Lukas likes to cook all manner of World foods.

