Place a Graphic in your Photoshop File
Often you’ll want to import existing graphics and artwork into your Photoshop document. A problem for Photoshop? Not at all — in fact, there are several ways you can do this!
External graphics can be placed in Photoshop as raster layers or Smart Objects. And in this solution, which has been adapted from the second chapter of my book, The Photoshop Anthology: 101 Web Design Tips, Tricks & Techniques, I’ll show you how to place these graphics, then we’ll talk about the difference between raster layers and Smart Objects.
Solution
Placing Artwork from a Web Page
Copy the artwork from the web page, then select Edit > Paste or press Ctrl-V (Command-V on a Mac) to paste it into your Photoshop document. Photoshop will create a new layer containing the artwork, or place it into a selected empty layer. The artwork will be on a raster layer.
Placing Artwork from Flattened Image Files
A flattened image file — such as a GIF, JPEG or PNG — contains artwork on a single layer. Open the file in Photoshop and use Select > All or press Ctrl-A (Command-A) to create a selection of the entire document. Click on your Photoshop document then select Edit > Paste or press Ctrl-V (Command-V) to paste it. Photoshop will paste the document into a new or selected empty layer as it does when pasting artwork from a web page. The artwork will be on a raster layer.
Placing Layers from a Different Photoshop Document
Position the document windows so that both are visible. Select the window of the document you wish to import from, to bring up its Layers palette. Select and drag the necessary layers over to the new window and release the mouse button when you see a thick, black outline around the window. This will copy the layers across as shown in the example at the top of the next page. The copied layers will retain their original properties.
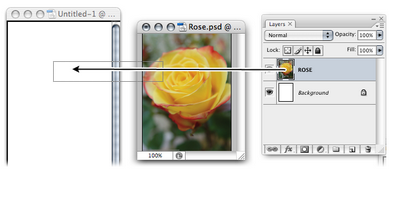
Placing Artwork from Illustrator
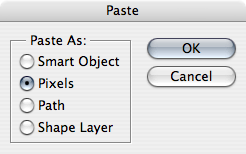
Open Illustrator and select the artwork you wish to export to Photoshop. Copy the artwork using Ctrl-C (Command-Con a Mac). Switch to Photoshop while Illustrator is still open and paste your copied artwork using Ctrl-V (Command-V). A dialog box will appear, asking you whether you wish to paste the artwork as a Smart Object, Pixels, Path or a Shape Layer.
Placing Artwork as a Smart Object
Select File > Place and choose the file you wish to import. Click Place to import the file into your Photoshop document as a Smart Object. For PDF and Illustrator files, Photoshop will display a dialog box that asks you to select the pages you wish to place. Choose the pages you want and click OK.
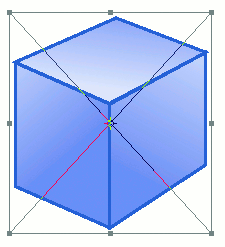
The Smart Object will initially be placed with a bounding box surrounding it, as shown here. You can use this bounding box to move, rotate, scale, or make other transformations to the object. When you’re done,double-click inside the bounding box to commit the Smart Object to its layer.
Discussion
Smart Objects
A Smart Object is an embedded file that appears in its own layer in Photoshop. A Smart Object layer is distinguished by an icon that overlays the thumbnail image displayed in the Layers palette, as shown in the example below.
Smart Objects are different from other layers because they are linked to a source file (e.g., an Illustrator file, JPEG, GIF or other Photoshop file). If you make changes to the source file, the Smart Object layer will also be updated with those changes.
![]()
In contrast, raster layers (or regular layers) are fully editable, so you can draw and paint on them, fill them with colors, or erase pixels. Unlike Smart Objects, where you retain image quality, if you resize a raster layer smaller, you will lose information.
This is demonstrated in the example on the next page, which shows the result of a Smart Object that has been decreased in size, then resized back to its original dimensions. The same steps, when applied to a raster layer, produce an image that is blurred and of lower quality.
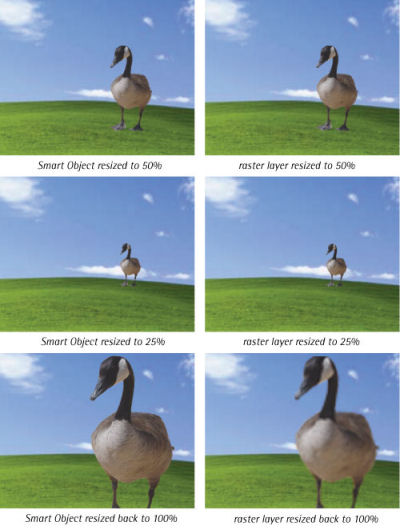

Because Smart Objects are linked to an outside document, you can resize them without losing the original image data. While you can apply layer effects and some transformations to Smart Object layers, you cannot actually manipulate (paint, draw, erase) their pixels because they are not editable from external documents. You can open the original source file for editing by double-clicking on the Smart Object icon.
Rasterizing
You can rasterize Smart Objects by right-clicking on the name of the Smart Object layer and choosing Rasterize Layer. This will break the link to the original source file and treat the layer as an ordinary raster layer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Placing Graphics in Photoshop
How can I resize an image in Photoshop without losing quality?
To resize an image in Photoshop without losing quality, you need to use the ‘Image Size’ option. Go to ‘Image’ in the top menu, then select ‘Image Size’. A dialog box will appear where you can adjust the width, height, and resolution. Make sure to check the ‘Resample’ box and select ‘Preserve Details 2.0’ from the dropdown menu. This will ensure that your image maintains its quality while being resized.
Can I import multiple images at once into Photoshop?
Yes, you can import multiple images at once into Photoshop. Go to ‘File’ > ‘Scripts’ > ‘Load Files into Stack’. Then, click ‘Browse’ to select the images you want to import. All selected images will be opened in separate layers in the same document.
How can I rotate an image in Photoshop?
To rotate an image in Photoshop, select the layer containing the image, then go to ‘Edit’ > ‘Transform’ > ‘Rotate’. You can then click and drag outside the bounding box to rotate the image. Hold down the Shift key while dragging to rotate in 15-degree increments.
How do I crop an image in Photoshop?
To crop an image in Photoshop, select the ‘Crop Tool’ from the toolbar. Click and drag to define the area you want to keep. You can adjust the crop area by dragging the handles on the corners and edges of the crop box. Once you’re satisfied with the crop area, press Enter to crop the image.
How can I add text to an image in Photoshop?
To add text to an image in Photoshop, select the ‘Text Tool’ from the toolbar. Click on the image where you want to add text and start typing. You can adjust the font, size, color, and other text properties in the options bar at the top of the screen.
How do I remove a background from an image in Photoshop?
To remove a background from an image in Photoshop, you can use the ‘Quick Selection Tool’ or the ‘Magic Wand Tool’ to select the background, then press Delete to remove it. If the background is complex, you might need to use the ‘Pen Tool’ to create a precise selection.
Can I edit a layer without affecting other layers in Photoshop?
Yes, you can edit a layer in Photoshop without affecting other layers. Any changes you make will only apply to the currently selected layer. If you want to apply changes to multiple layers at once, you can link them together by selecting the layers and clicking the ‘Link Layers’ button in the Layers panel.
How do I save an image with a transparent background in Photoshop?
To save an image with a transparent background in Photoshop, you need to save it in a format that supports transparency, such as PNG. Go to ‘File’ > ‘Save As’, choose PNG from the ‘Format’ dropdown menu, and make sure ‘Transparency’ is checked in the ‘PNG Options’ dialog box.
How can I change the color of an object in Photoshop?
To change the color of an object in Photoshop, you can use the ‘Hue/Saturation’ adjustment. Select the layer containing the object, then go to ‘Image’ > ‘Adjustments’ > ‘Hue/Saturation’. You can then adjust the hue slider to change the color.
How do I undo a mistake in Photoshop?
To undo a mistake in Photoshop, you can use the ‘Undo’ command by pressing Ctrl+Z (or Command+Z on a Mac). If you want to undo multiple steps, you can use the ‘History’ panel, which allows you to revert back to any previous state of your image.
Corrie is the lead designer and developer for PixelMill. This would-be triathlete has a mathematics degree but wishes she had double-majored in computer science and art instead. Maybe next time...
Published in
·Accessibility·Design·Design & UX·Freelancing·Illustration·Sketch·Software·UI Design·Usability·UX·Web·March 23, 2016


