- CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black)
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue)
- Lab Color
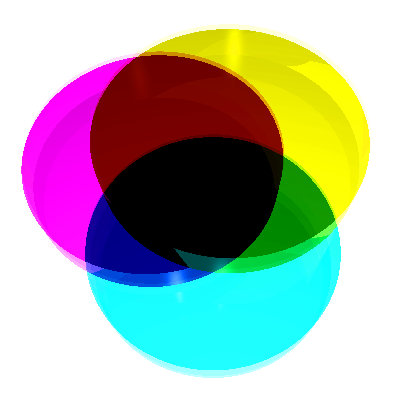 CMYK is known as a “subtractive” color model. White is the natural color of the paper or other background, while black results from a full combination of colored inks.
CMYK is known as a “subtractive” color model. White is the natural color of the paper or other background, while black results from a full combination of colored inks.
 The separations below, on the left use maximum black and a minimal amount of cyan, magenta and black. On the right are separations for printing with process cyan, magenta, and yellow inks.
The separations below, on the left use maximum black and a minimal amount of cyan, magenta and black. On the right are separations for printing with process cyan, magenta, and yellow inks.

 Images from Wikipedia
2. The RGB model is used when working with screen based designs. A value between 0 and 255 is assigned to each of the light colors, Red, Green and Blue. So for example, if you wanted to create a purely blue color, Red would have a value of 0, Green would have a value of 0 and Blue would have a value of 255 (pure blue). To create black, Red, Green and Blue would each have a value of 0 and to create white, each would have a value of 255. RGB is known as an “additive” model and is the opposite of the subtractive color model.
Images from Wikipedia
2. The RGB model is used when working with screen based designs. A value between 0 and 255 is assigned to each of the light colors, Red, Green and Blue. So for example, if you wanted to create a purely blue color, Red would have a value of 0, Green would have a value of 0 and Blue would have a value of 255 (pure blue). To create black, Red, Green and Blue would each have a value of 0 and to create white, each would have a value of 255. RGB is known as an “additive” model and is the opposite of the subtractive color model.
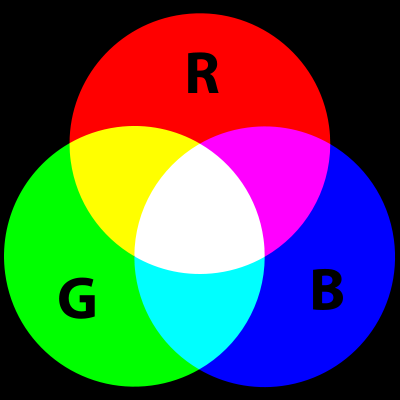 In this situation, when we talk of “value” of color, we’re referring to the strength of the colors in relation to each other. In the image below, you can see a photograph separated into its red, green and blue elements.
In this situation, when we talk of “value” of color, we’re referring to the strength of the colors in relation to each other. In the image below, you can see a photograph separated into its red, green and blue elements.
 Image from Wikipedia
3. The Lab color model is a slightly more complex beast. It is made up of three components – the lightness component (L) ranging from 0 to 100, the “a” component comes from the green-red axis in the Adobe Color Picker, and the “b” component which comes from the blue-yellow axis in the Adobe Color Picker. Both “a” and “b” can range from +127 to –128. When Photoshop is converting from one model to another, it uses Lab as the intermediate color model.
So, after all that which model should you use?
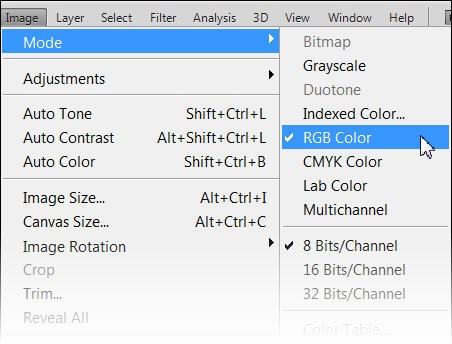
If you know that your work is being sent to a commercial printer, then it’s a good idea to start your document in CMYK mode. Otherwise it’s safe to say that you can work in RGB for almost any other non-printing project. It is possible to convert from one color model to another but as RGB and CMYK spaces are both device-dependent spaces, the conversion formula is not that simple and requires a color management system (such as Photoshop or other graphics editor) using color profiles and that is why conversions are rarely exact. If you do need to convert from one color model to the other, it’s just a matter of choosing Image > Mode and then picking the one you need.
Image from Wikipedia
3. The Lab color model is a slightly more complex beast. It is made up of three components – the lightness component (L) ranging from 0 to 100, the “a” component comes from the green-red axis in the Adobe Color Picker, and the “b” component which comes from the blue-yellow axis in the Adobe Color Picker. Both “a” and “b” can range from +127 to –128. When Photoshop is converting from one model to another, it uses Lab as the intermediate color model.
So, after all that which model should you use?
If you know that your work is being sent to a commercial printer, then it’s a good idea to start your document in CMYK mode. Otherwise it’s safe to say that you can work in RGB for almost any other non-printing project. It is possible to convert from one color model to another but as RGB and CMYK spaces are both device-dependent spaces, the conversion formula is not that simple and requires a color management system (such as Photoshop or other graphics editor) using color profiles and that is why conversions are rarely exact. If you do need to convert from one color model to the other, it’s just a matter of choosing Image > Mode and then picking the one you need.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Color Models
What is the difference between additive and subtractive color models?
Additive and subtractive color models are two different ways of mixing colors. The additive model, which includes RGB (Red, Green, Blue), works by adding colors together to create white. This model is used in light-emitting sources like screens and monitors. On the other hand, the subtractive model, which includes CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black), works by subtracting colors from white to create black. This model is used in color printing and mixing paints.
How does the HSV color model differ from the RGB model?
The HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) color model represents colors in a way that is more intuitive and closer to how humans perceive color. Unlike RGB which defines color based on primary colors, HSV defines color based on hue (the type of color), saturation (the intensity of the color), and value (the brightness of the color). This makes it easier to create and manipulate shades and tints of a particular color.
What is the YIQ color model and where is it used?
The YIQ color model is used in the NTSC (National Television System Committee) color TV system, primarily in North America. It separates the color signal (I and Q) from the luminance signal (Y), allowing black and white TVs to display the luminance while ignoring the color information. This model is less commonly used in graphic design or digital media.
Why is the Pantone color model important in the design industry?
The Pantone color model is a proprietary, standardized color system used across various industries, particularly in graphic design, fashion, and product design. It provides a universal language of color that enables designers, manufacturers, retailers, and customers to accurately communicate and reproduce specific colors.
How does the CMYK color model work in printing?
The CMYK model works by mixing different percentages of Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (black) inks to create a wide range of colors. It’s a subtractive model, meaning it subtracts brightness from white. As more color is added, the result becomes darker. This model is the standard for most forms of color printing.
Why does the RGB color model dominate in digital displays?
The RGB model is an additive color model, meaning colors are created by combining light. Since digital screens emit light, the RGB model is ideal for creating a wide range of colors. By varying the intensity of red, green, and blue light, almost any color can be produced.
What is color gamut in relation to color models?
Color gamut refers to the complete range of colors that can be produced by a color model or a specific device, like a monitor or printer. Different devices have different color gamuts, meaning they can display or print a different range of colors.
How does color perception affect the use of color models?
Human color perception can vary greatly depending on lighting conditions, individual differences, and cultural factors. Therefore, color models are used to standardize the way colors are represented and reproduced, ensuring consistency across different mediums and devices.
What is the role of color profiles in color models?
Color profiles are sets of data that ensure colors are represented consistently across different devices. They define how a device interprets and displays color information from a color model. Without color profiles, the same color could look different on two different screens or when printed.
How do color models relate to color theory in design?
Color models provide a practical framework for applying color theory in design. They allow designers to understand and manipulate color in a systematic way, enabling them to create specific moods, highlight important elements, and achieve aesthetic balance in their designs.
Jennifer Farley is a designer, illustrator and design instructor based in Ireland. She writes about design and illustration on her blog at Laughing Lion Design.




